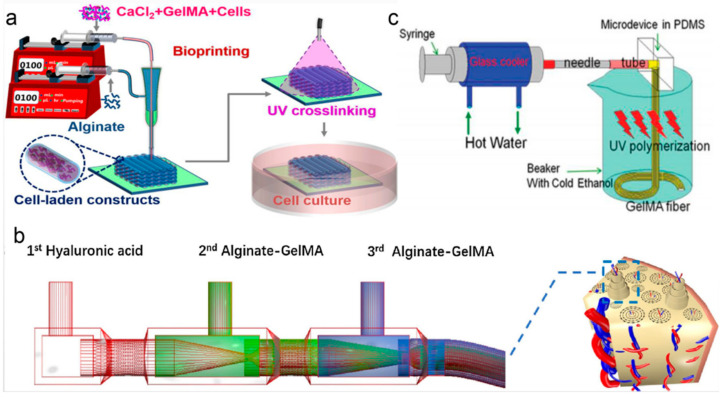
Figure 1.
(a) Extrusion method: strategy of bioprinting GelMA/alginate core/sheath microfibers into 3-D constructs with tunable microenvironments. Reproduced with permission [57]. (b) Laminar flow-based method: Capillary microfluidic device used for biomimetically constructing osteon-like double-layer hollow microfiber with the novel composite bioink. Reproduced with permission [59]. (c) Electrospinning method: The microdevice to generate microstructured GelMA fibers. Reproduced with permission [60].