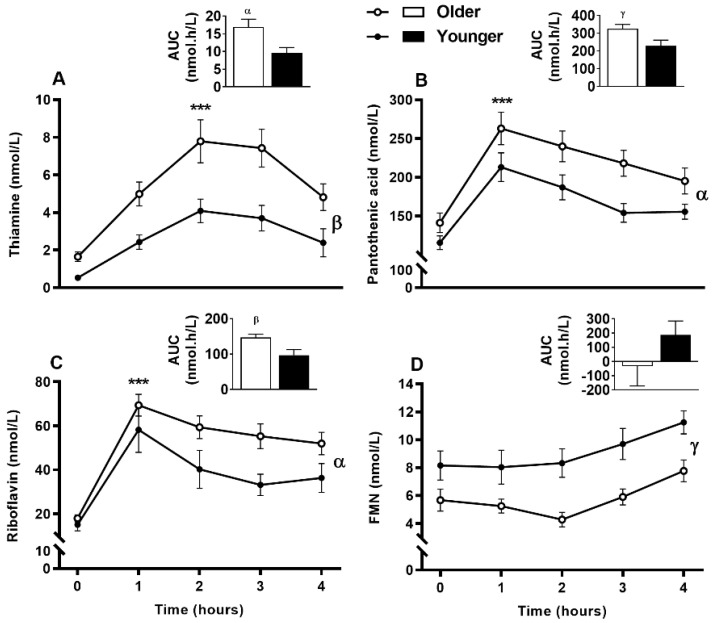
Figure 5.
Plasma response of (A), thiamine (B), pantothenic acid (C), riboflavin, and its vitamer (D), flavin mononucleotide (FMN) at fasting (time, 0), hourly until four hours (time, 1, 2, 3, 4) and the four hour incremental area under the curve (AUC, represented by bar-graphs) following a single multivitamin and mineral supplement ingestion in older and younger adults. Data for multiple time points was compared using general linear mixed model with time as repeated and age as fixed factors. AUC data was compared with general linear univariate analysis of variance with age as fixed factor. ***, p < 0.001, significant increase following supplement intake relative to baseline in both age groups. The older adults had increased postprandial thiamine (age effect p = 0.001, time effect p < 0,001), pantothenic acid (age effect p = 0.008, time effect p < 0.001) and increased riboflavin (age effect p = 0.026, time effect p < 0.001) than the younger adults (α, p < 0.05; β, p < 0.01; γ, p < 0.001, main age difference).