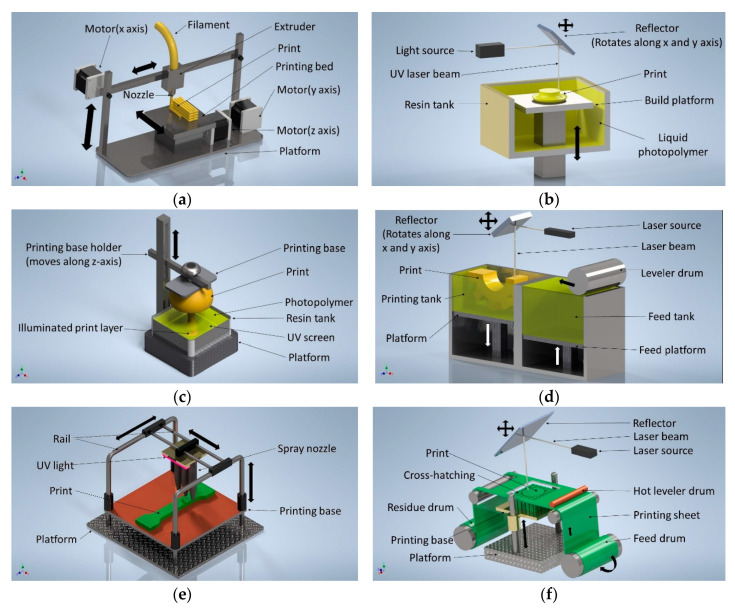
Figure 1.
Selected techniques for polymer AM. (a) The Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printers work on the materials extrusion principle to print desired parts. (b) The stereolithography (SLA) technique uses a UV laser beam to cure liquid UV curable polymer for printing with high accuracy. (c) The digital light processing (DLP) printers print highly accurate parts using UV screens and are less time consuming than the SLA. (d) The selective laser sintering (SLS) fuses fine powder polymers with a laser beam. However, the printed parts produce rough or grainy surfaces. (e) In the polyjet printing process, fine drops of polymers are sprayed by multiple nozzles on the printing bed which are immediately cured by the UV light. It is capable of fast printing with multi-material deposition. (f) In the sheet lamination (LOM), sheets of polymers are precisely cut and added in layers to make the final product. When fast printing and large size printing capability are required, the LOM technique is preferred.