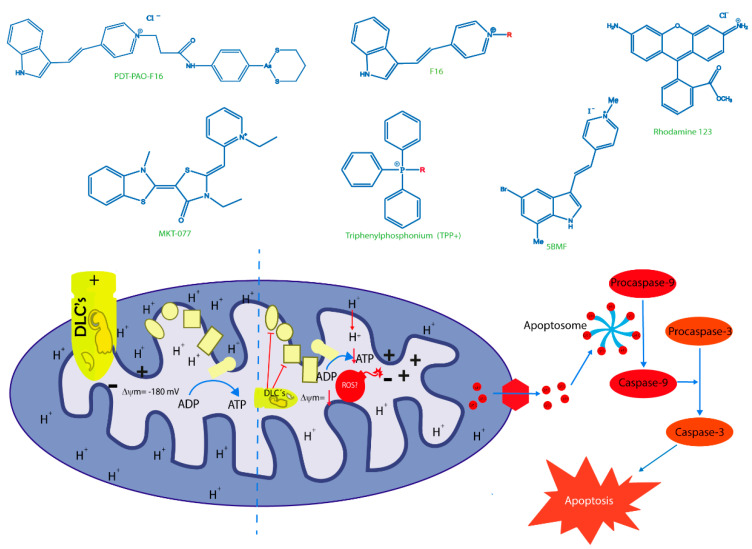
Figure 2.
Principal delocalized lipophilic cations (DLCs) and their mechanism of action. The figure shows the chemical structures of classic lipophilic cations as Rhodamine 123, TPP+ and MKT-077. Additionally, the chemical structures of novel DLCs, such as 5BMF, F16 and their derivative PDT-PAO-F16, are shown. Lower section shows ΔΨm as the attraction force that allows all DLCs to reach tumor cell mitochondria and their respective targets described for each of them. The final effect of mitochondrial malfunctions induced by DLCs is cell death, principally through apoptosis. + positive charge in mitochondrial intermembrane space; (−) negative charge on the matrix side of the inner mitochondrial membrane; red arrows: H+ transposed from intermembrane space to mitochondrial matrix and a decrease in mitochondrial transmembrane potential; inhibitory red lines: inhibitory effects of delocalized lipophilic cations.