Figure 8.
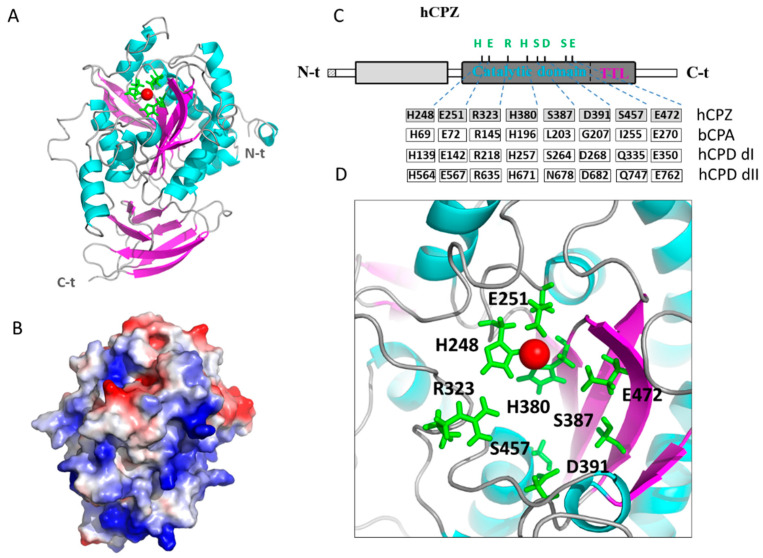
Structural modeling of the catalytic and transthyretin-like (TTL) domains of human CPZ. (A) Ribbon representation of human CPZ structure showing the central catalytic moiety at the top and the C-terminal TTL domain at the bottom. The side chains of the three residues involved in the Zn2+ binding (i.e., His248 Glu251, His380) are indicated in green; (B) Electrostatic surface potential distribution of the catalytic domain of human CPZ (in the same orientation as panel A). Blue indicates positive and red indicates negative charge potential; (C) Linear representation of the full-length human CPZ, showing the location of relevant amino acids involved in the catalytic mechanism and substrate binding (Arg323, Ser387, Asp391, Ser457, and Glu472), as well as in zinc binding (His248 Glu251, His380). Residues found in equivalent positions in bovine CPA (bCPA, as reference), in domain I of human CPD (hCPDdI) and domain II of human CPD (hCPDdII) are indicated; (D) Magnification of the active site of human CPZ, showing the location of these residues important for the catalytic mechanism and substrate specificity determination. The Zn2+ metal ion is shown in all representations as a red sphere.