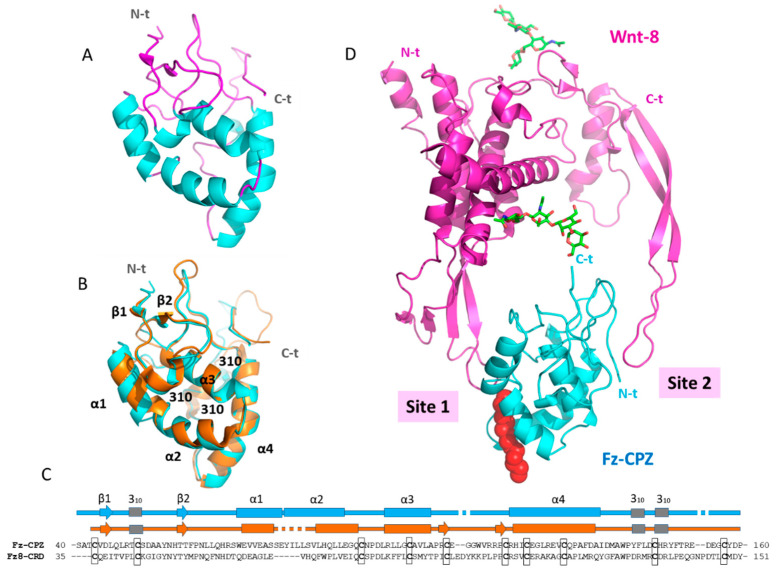
Figure 9.
Structural modeling of the Fz domain of human CPZ and its interaction with Wnt-8. (A) Ribbon representation of the highly conserved N-terminal Fz domain of human CPZ; (B) Structural comparison of the Fz domain of human CPZ (Fz-CPZ, represented in blue) and the cysteine-rich domain of mouse Fz8 (Fz8-CRD, represented in orange); (C) Structure-based sequence alignment of Fz-CPZ and Fz8-CRD (represented in blue and orange respectively); (D) Ribbon representation of Wnt-8 in a proposed complex with the Fz domain of CPZ. The extended palmitoleic acid (PAM) group is represented with red spheres, and the most important sites of interaction between Fz-CPZ and Fz8-CRD are indicated as Site 1 and Site 2. For all proteins, the N-terminus and C-terminus are indicated as N-t and C-t, respectively.