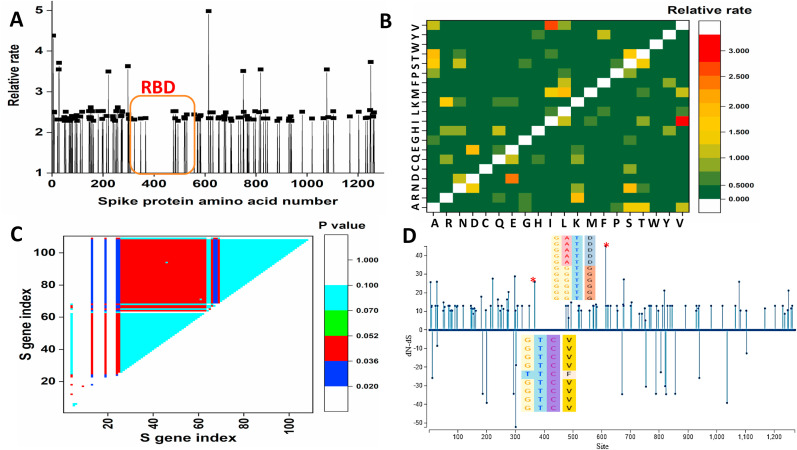
Fig. 2.
(A) Distribution of relative rate on each residue of SARS-CoV2 spike protein (B) The relative rate value for the substitution of an amino acid to another one calculated from the maximum likelihood analysis. (C) Identification of the SARS-CoV2 S gene under positive selection bias by using the codon-based test. The probability of rejecting the null hypothesis of strict-neutrality in favor of the alternative hypothesis for positive selection is shown in different colors. (D) Selection site analysis of SARS-CoV2 spike protein under the positive selection bias. Corresponding alignment at the particular codon position (indicated by ∗) under high positive selection bias is shown. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)