Figure 1.
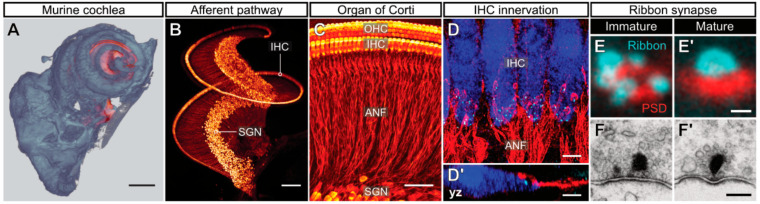
Structural overview of the peripheral auditory pathway. Light-sheet microscopic 3D- reconstructions of (A) the bony murine cochlea that harbors the organ of Corti and (B) the isolated peripheral auditory system, with afferent spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs) branching out towards the row of inner hair cells (IHCs), in the typical spiraling staircase anatomy. IHCs and SGNs are labeled with an antibody against the cytosolic Ca2+-buffer Calretinin. (C) Confocal maximum projection of the organ of Corti labeled for the cytosolic Ca2+-buffer Parvalbumin, displaying the three rows of outer hair cells (OHCs), the single row of IHCs and the afferent innervation (auditory nerve fibers; ANF) by the SGNs. (D) Innervation of IHCs (Calbindin; blue) by individual SGN neurites (a3-Na+/K+-ATPase; red), showing the presynaptic ribbons (CtBP2; cyan) in contact with the postsynaptic SGN boutons. (D’) Side view of the innervated IHC showing the basolateral position of the synaptic ribbon and connected bouton. (E,E’) STED microscopic images of IHC synaptic ultrastructure of (E) a developing IHC active zone distributed in several precursor spheres colocalizing with multiple clusters of the postsynaptic density (PSD) versus (E’) one large ribbon opposing one ellipsoid PSD in a mature preparation. (F,F’) Electron microscopic images of (F) immature multi-ribbon active zones with roundish profiles versus (F’) the wedge-shape of a mature IHC ribbon that is attached to the curved presynaptic membrane. Scale bars: A 300 µm; B 150 µm; C 50 µm; D-D’ 5 µm; E-E’ 250 nm; F-F’ 200 nm. (B,E,E’) with permission from Reference [4]; (D) with permission from Reference [5].