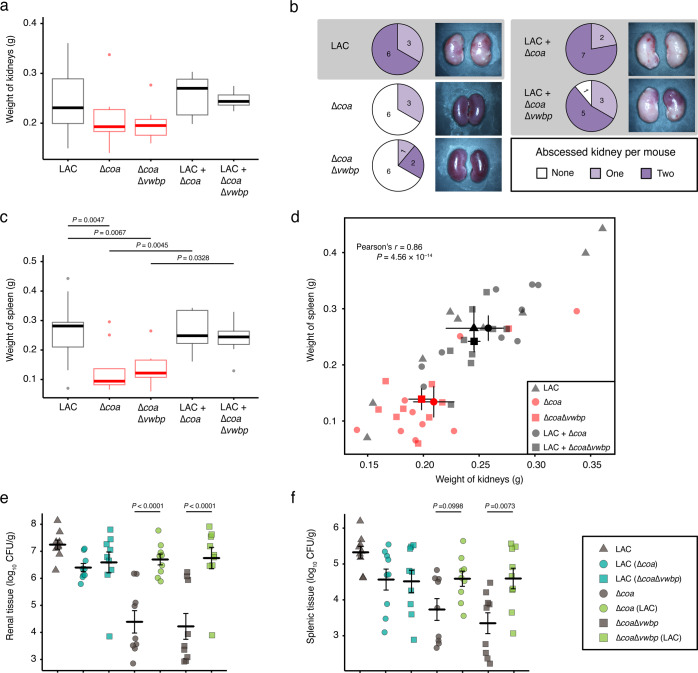
Fig. 1. Coagulases contribute to staphylococcal persistence, disease progression, and organ inflammation.
Mice (n = 9 for each cohort) were injected in their retro-orbital sinus with 1 × 106 CFU of LAC, Δcoa, or ΔcoaΔvwbp; and cocultures of LAC and Δcoa, or LAC and ΔcoaΔvwbp. On Day 15 post infection, the kidneys and spleens were excised, gross-examined, photographed, homogenized and spread on selective agar for enumeration of CFUs. The data represent two trials. a Pyelonephritis plotted as the weight of each pair of kidneys (adjusted P values calculated using general linear hypotheses test with manual contrast). b Number of mice that had abscesses on either one or both of their kidneys; images are of kidneys representing the pathology observed within each cohort. c Splenomegaly plotted as the weight of each spleen (adjusted P values calculated using general linear hypotheses test with manual contrast). d Plot showing Pearson correlation between splenomegaly and pyelonephritis. Staphylococcal load in e kidneys and f spleens plotted as log10 CFU per gram of tissue (adjusted P values calculated using general linear hypotheses test with manual contrast, error bars denote ±SEM). Boxplot elements are: center line–median; box limits–upper and lower quartiles; whiskers–1.5×interquartile range; points–outliers.