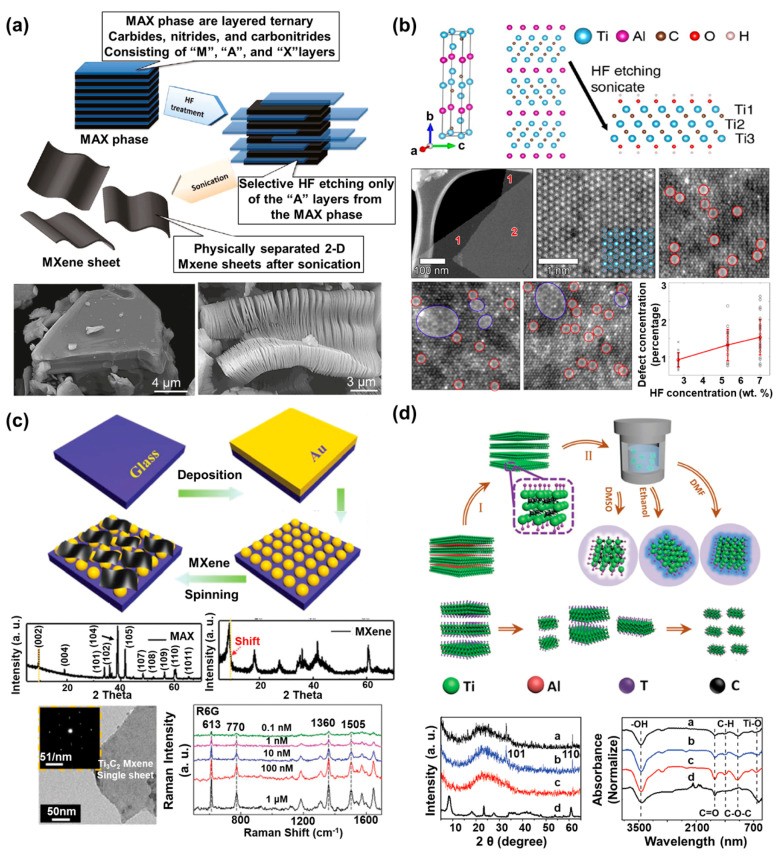
Figure 2.
Definition and characteristics of MXenes. (a) Schematic diagram of the synthesis process from the MAX phase to the MXene nanosheets, and SEM images of the MAX phase (Ti3AlC2) before and after hydrofluoric acid (HF) treatment (reprinted with permission from [37]; copyright (2012) American Chemical Society). (b) Crystal structure images of the MAX phase of Ti3AlC2, and the low-magnification and atomic resolution high-angle annular dark field (HAADF)-scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) images of Ti3C2Tx (reprinted with permission from [39]; copyright (2016) American Chemical Society). (c) Schematic image of the MXene/Au nanostructure (NS) SERS substrate fabrication process, XRD pattern, and TEM image of synthesized MXene (Ti3C2Tx), and the Raman spectra of R6G on the MXene/Au NSs SERS substrate with different concentration ranges of R6G (reprinted with permission from [45]; copyright (2019) The Royal Society of Chemistry). (d) Schematic image of the MXene-derived quantum dot (MQD) synthesis process using different solvents such as the dimethylformamide (DMF), DMSO, and ethanol (f-MQDs, s-MQDs, and e-MQDs, respectively), and the XRD pattern and FTIR spectra of the e-MQDs (black), f-MQDs (blue), and s-MQDs (red) (reprinted with permission from [41]; copyright (2018) John Wiley and Sons, Inc.).