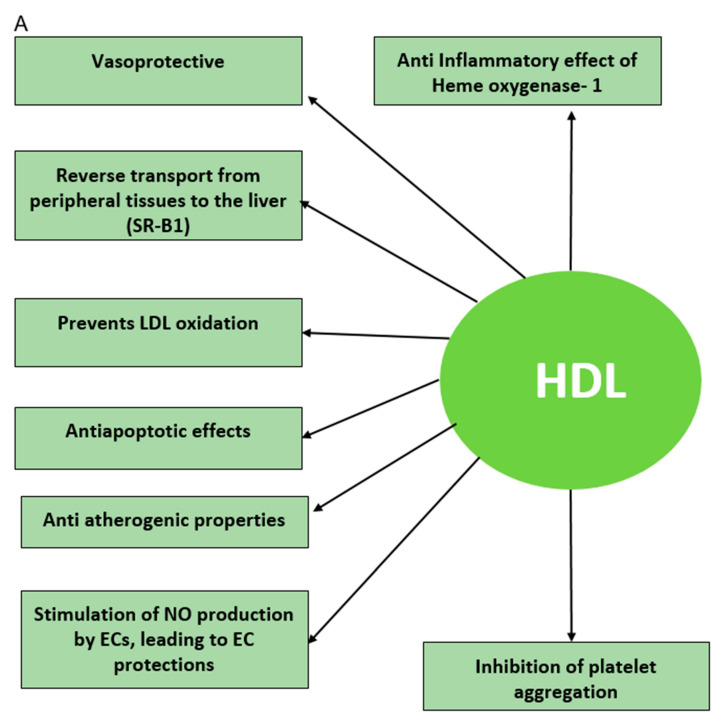
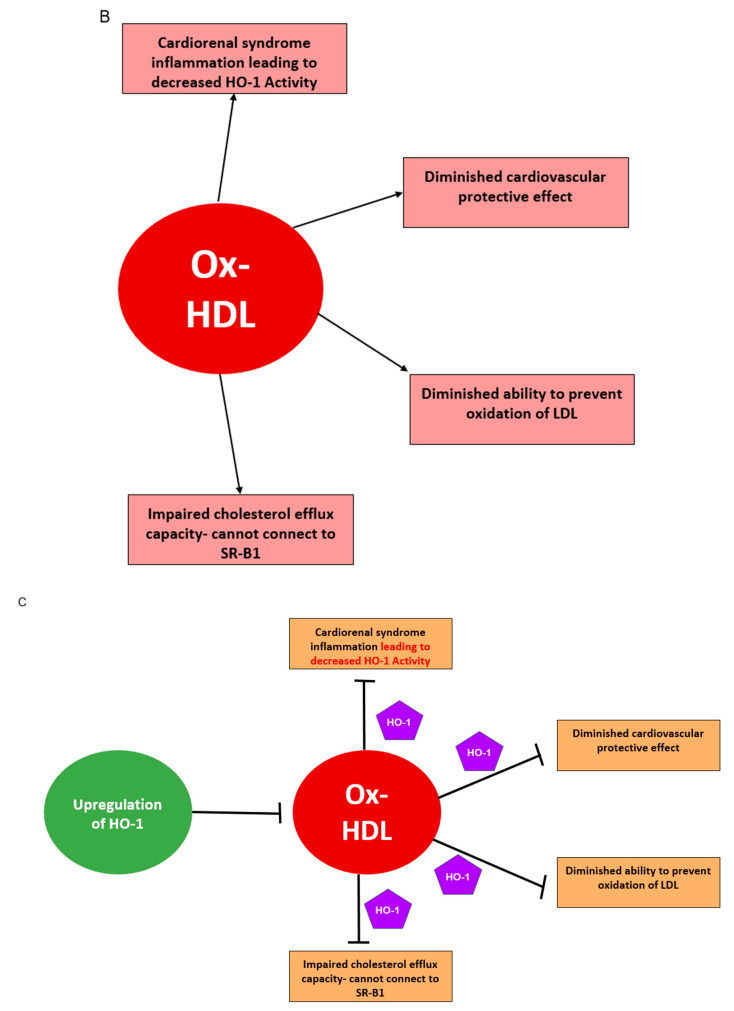
Figure 1.
(A) The beneficial effects of high-density lipoprotein (HDL). HDL exhibits protective effects through multiple mechanisms, including lowering tissue cholesterol levels through reverse cholesterol transport, attenuation of LDL oxidation, and decreasing inflammatory responses. (B) The adverse effects of oxidized HDL (Ox-HDL). Oxidized or dysfunctional HDL is proinflammatory and atherogenic. (C) Role of HO-1. HO-1 has a protective effect against reactive oxygen species (ROS) and oxidative stress, and the upregulation of HO-1 decreases the detrimental effects of oxidized HDL. HO-1 = heme oxygenase 1; SR-B1 = scavenger receptor class B type 1; HDL=high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL = low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; NO = nitric oxide; EC = endothelial cells.