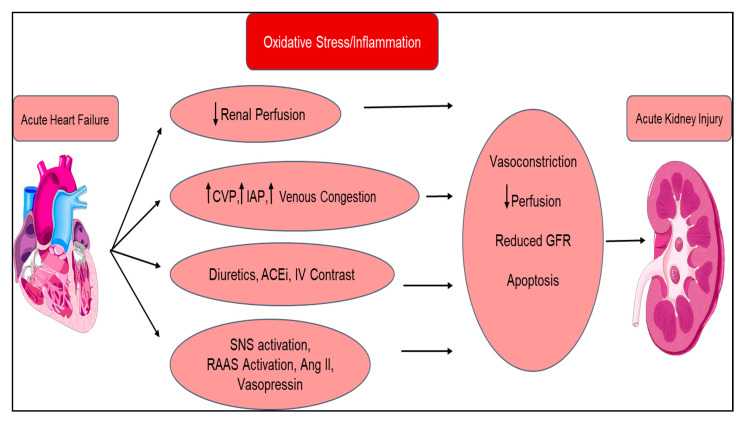
Figure 2.
Pathophysiology of acute cardiorenal syndrome (type 1): mechanism of how acute heart failure leads to acute kidney injury (AKI) due to inadequate renal perfusion, endothelial activation, and cytokine production, which activates the RAAS, salt and water imbalance, and vasoconstriction, further exacerbating AKI. CVP = central venous pressure; IAP = intraabdominal pressure; ACEi = angiotensin converter enzyme inhibitor; RAAS = renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system; SNS = sympathetic nervous system; GFR = glomerular filtration rate.