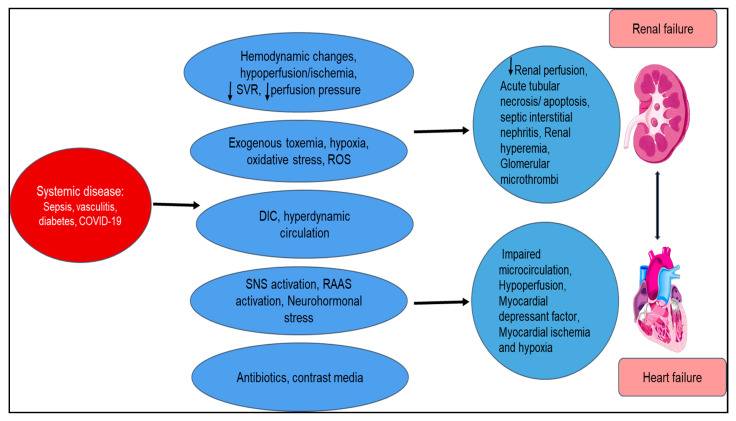
Figure 6.
Summary of the pathophysiology of secondary cardiorenal syndrome (type 5): mechanism is characterized by combined cardiac and renal failure due to acute or chronic processes that cause hemodynamic instabilities, hypercoagulability, neurohormonal imbalances, and toxicity and hypoxia that cause poor renal perfusion, myocardial ischemia, and hypoxia. SVR = systemic vascular resistance; ROS = reactive oxygen species; DIC = disseminated intravascular coagulation; SNS = sympathetic nervous system; RAAS = renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system.