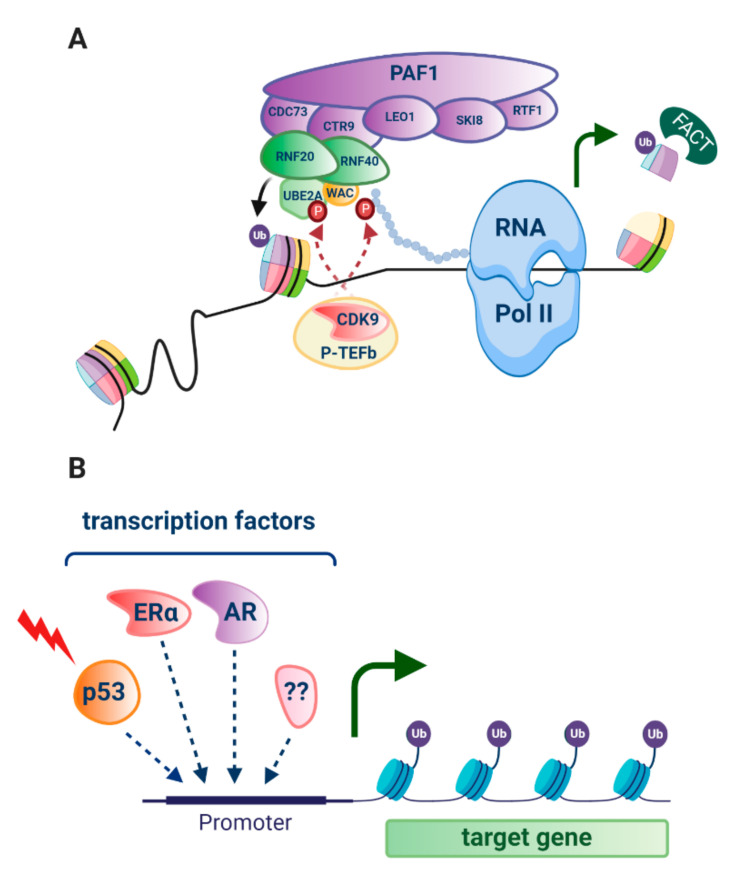
Figure 2.
H2Bub1 in transcriptional elongation. (A) Following stimuli such as DNA damage, hormones or developmental signals, cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (CDK9) that is part of the Positive Transcription Elongation Factor-b (P-TEFb) complex phosphorylates Ser2 in the carboxy-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II (RNA pol II) depicted by a chain of circles, as well as the E2 ubiquitin conjugating enzyme ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 A (UBE2A). This dual phosphorylation shown by red circles, establishes a binding domain for the WW domain-containing adaptor with coiled-coil (WAC) and the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex RNF20/RNF40 that monoubiquitinates histone H2B at lysine 120 (H2Bub1, ubiquitin shown as a purple circle). RNF20/RNF40 physically interacts with the PAF1 complex consisting of CDC73, CTR9, LEO1, SKI8, RTF1 and PAF1 that associates with RNA pol II to establish transcriptional elongation. The chromatin remodelling factor FACT is recruited by H2Bub1, and removes a H2B-H2A dimer from the core nucleosome that takes away the physical block to RNA pol II, allowing it to move through the nucleosome, facilitating gene expression (green arrow). (B) A number of transcription factors have been associated with enriched H2Bub1 at target genes, including p53 (red lightning bolt depicts DNA damage that activates this tumour suppressor), the estrogen receptor (ERα) and androgen receptor (AR). ?? indicates as yet unknown transcription factors. Created with BioRender.com.