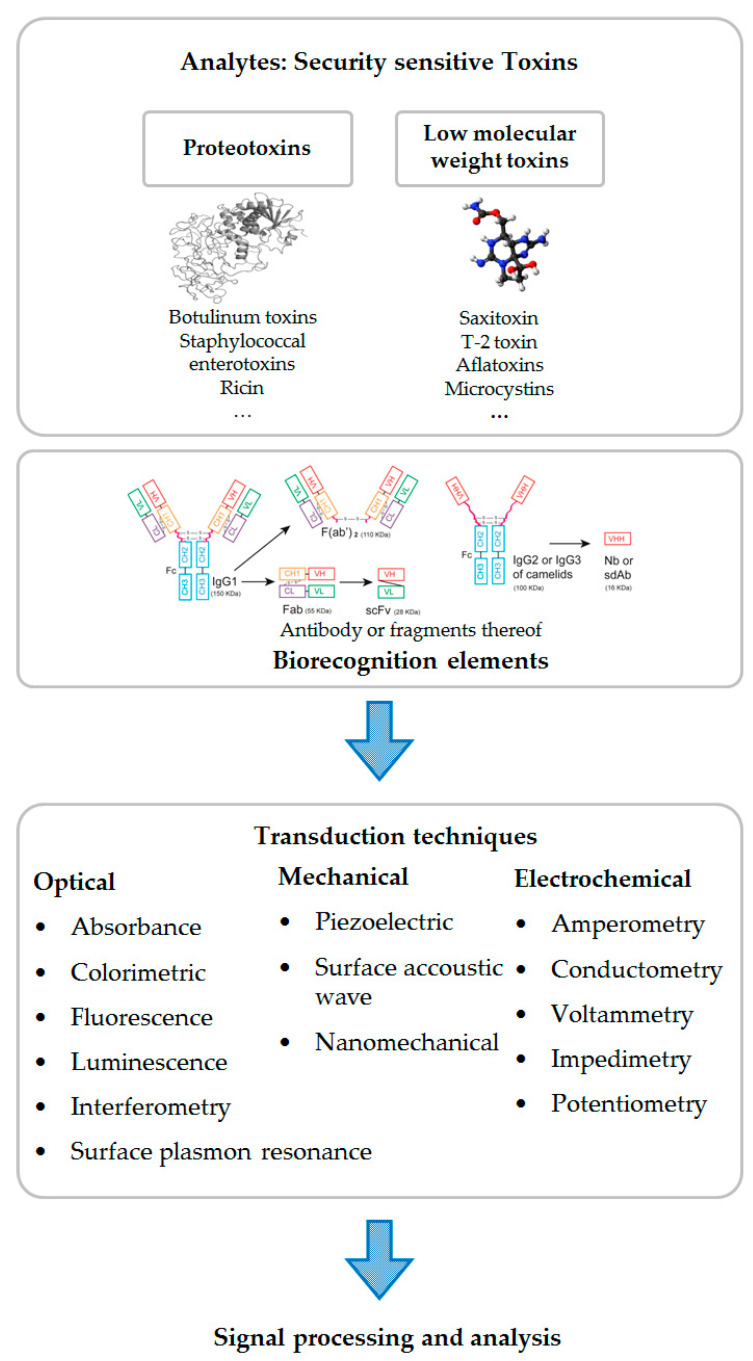
Figure 1.
General overview of immunosensor components for detection of security sensitive toxins as analyte (3D structure model of ricin (pdb: 2AAI [30]) as well as a ball-and-stick model of saxitoxin are depicted). Because this review is focused on immunosensors, antibodies (or fragments of antibodies) (VL: variable light chain; VH: variable heavy chain; CL: constant light chain; CH: constant heavy chain; Fab: antigen binding fragment; scFv: single-chain variable fragment; VHH: variable domain of heavy chain antibody; Nb: nanobody; sdAb: single domain antibody) are depicted as biorecognition elements only (Adapted from [31]. MDPI (2014)). For the sake of completeness, it should be noted that alternative biorecognition elements, such as aptamers, natural receptor proteins, carbohydrates or cell-based receptors, could also be employed for toxin detection. Several examples of possible transduction mechanisms are noted as well as signal processing.