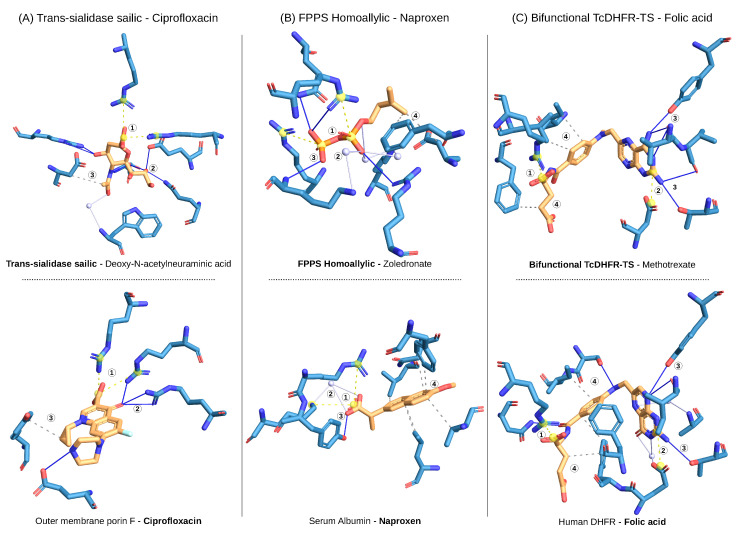
Figure 3.
Non-covalent interaction patterns accounting for the repositioning predictions. The structure-based drug repositioning approach predicted that ciprofloxacin binds trans-sialidase (sialic acid site), naproxen binds FPPS (homoallylic site) binder, and folic acid binds TcDHFR. The repositioning is based on the similarity of the non-covalent interactions defining the binding mode of inhibitors (orange) to their targets (blue) between query (top) and hit (bottom) complexes. (A) The binding mode of ciprofloxacin to porin F (PDB ID: 4kra) is similar to the one of deoxy-N-acetylneuraminic acid to trans-sialidase (sialic acid site) (PDB ID: 1ms0). Both have in common (1) a double salt bridge (yellow dashed lines), (2) a triple set of hydrogen bonds (blue lines), and (3) a hydrophobic interaction (gray dashed lines). In the same way, (B) the binding mode of naproxen to serum albumin (PDB ID: 4ot2) is similar to the one of zoledronate to FPPS (PDB ID: 3iba) as they have (1) two salt bridges, (2) one water bridge (lightblue lines and sphere), and (3) one hydrogen bond in common. (C) The binding mode of folic acid to human DHFR (PDB ID: 1drf) is similar to the one of methotrexate to TcDHFR (PDB ID: 3cl9) with (1,2) two salt bridges, (3) a set of hydrogen bonds, and (4) a set of hydrophobic interactions.