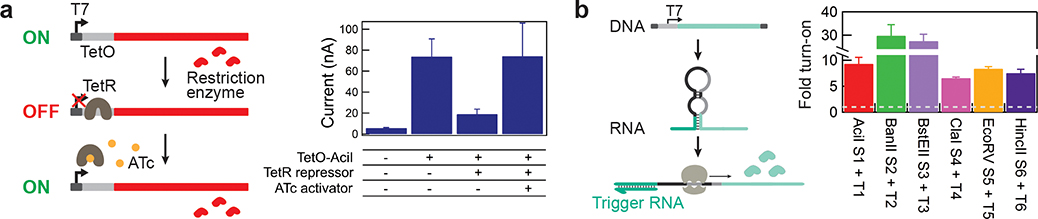
Figure 4. Application of the gene-circuit electrochemical interface for small molecule- and RNA-actuated electrochemical signaling.
a. Anhydrotetracycline (ATc)-mediated derepression of TetR-regulated TetO expression of the restriction enzyme-based reporter AciI (left). ATc-dependent induction (40 μM) of electrochemical signaling on-chip (right). Data represents the mean ±SE of three replicates. b. Toehold switches specific to synthetic RNA sequences were designed to control the expression of six different restriction enzyme-based reporters. RNA-dependent activation of toehold switches induces electrochemical signaling. Dotted line indicates switch alone negative controls. All electrochemical measurements were performed with square wave voltammetry and peak current is used for calculation of fold turn-on. Data represents the mean ±SE of three replicates.