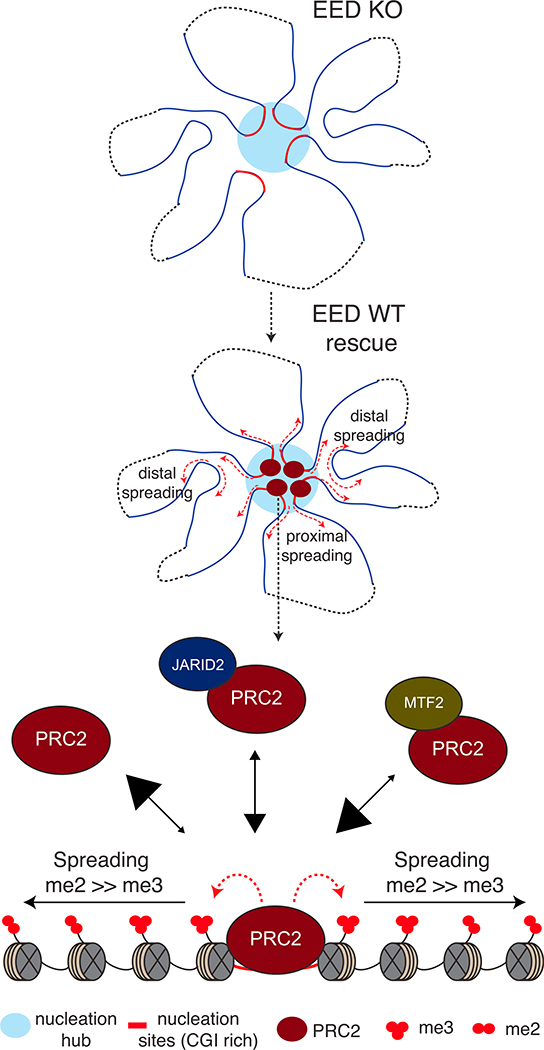
Figure 7. Model for PRC2 Recruitment to Chromatin and Establishment of H3K27me2/3 Domains.
In EED KO mESCs, spatial interactions among some, but not all nucleation sites are lost. Upon expression of EED, PRC2 is first recruited to regions called “nucleation hubs” that have a specific subset of CGIs forming spatial clusters in the nucleus. The stable binding of PRC2 to chromatin depends on its on and off rates, shown by arrows pointed “to” and “from” chromatin, respectively, with the size of the arrowheads reflecting relative PRC2 binding. PRC2 alone exhibits the lowest stability on chromatin, but its stability is increased when complexed with Jarid2 and further increased when complexed with MTF2. Upon reaching sufficient concentrations, PRC2 catalyzes H3K27me2 first and converts it to H3K27me3 at the nucleation sites, where it is more stably bound. From this initial nucleation event, PRC2 rapidly spreads H3K27me3 proximal to and H3K27me2 distal to the nucleation sites.