Figure 5.
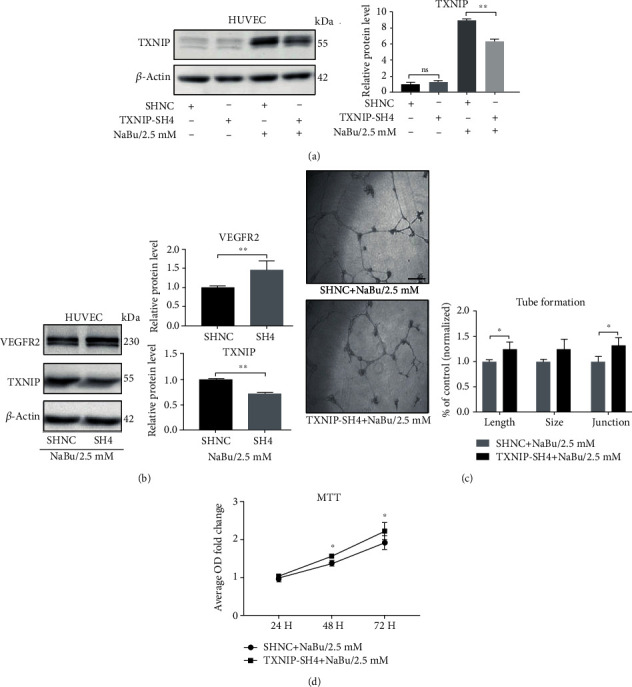
TXNIP knockdown promotes the VEGFR2 expression and partially restores the angiogenesis in context of NaBu treatment. (a) Western blot was used to confirm shRNA knockdown efficiency of TXNIP in HUVEC cells in context of NaBu treatment (left). Relative grey values were used for the statistical analysis (right) (∗∗P ≤ 0.01). (b) HUVEC cells stably expressing TXNIP shRNA were treated with designated concentration of NaBu, and cell lysates were subjected to western blot analysis with anti-VEGFR2 or anti-TXNIP antibody. Beta-actin was used as a loading control. Relative grey values were used for the statistical analysis (∗∗P ≤ 0.01). (c) Tube formation assay was performed with stable cell lines either expression TXNIP shRNA or scramble shRNA (control). Those two cell lines were treated with 2.5 mM NaBu, and the tube formation status was pictured (left). ImageJ was used to statistically analyzed the values of length, size, and junction of tube formation of HUVEC cells (∗P ≤ 0.05, bar: 400 μm) (right). (d) MTT assay was carried out to evaluate the effect of NaBu on stable HUVEC cell lines proliferation with either TXNIP knockdown or scramble control (n = 5‐8, ∗P ≤ 0.05). SHNC: scramble shRNA control; TXNIP-SH4: TXNIP shRNA.
