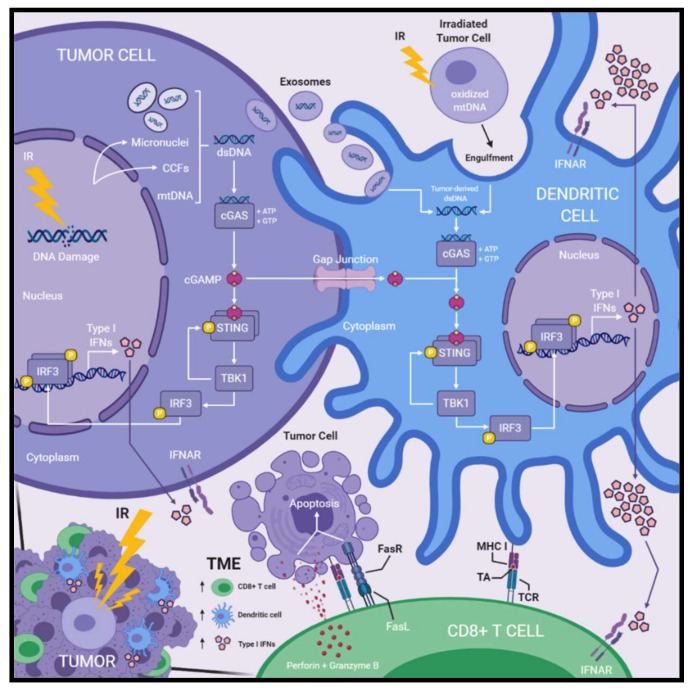
Figure 1.
Radiation-induced DNA damage activates cGAS–STING signaling, type I interferon production, and immune activation within the tumor microenvironment. Radiation-induced DNA damage leads to accumulation of cytosolic dsDNA within irradiated tumor cells. Micronuclei, CCFs, and mtDNA have been reported as sources of cytosolic dsDNA. cGAS detects cytosolic dsDNA and produces cGAMP, a secondary messenger molecule formed by phosphodiester linkages between ATP and GTP molecules. cGAMP binding of STING induces conformational changes that enable the recruitment of TBK1, which then phosphorylates STING. Phosphorylated STING recruits IRF3, which is next phosphorylated by TBK1. Phosphorylated IRF3 dimerizes and translocates to the nucleus where it functions as a transcription factor for the expression of type I IFNs. Following irradiation of tumor cells, DCs acquire tumor-derived dsDNA within the cytosol via internalizing tumor-derived exosomes or engulfment of irradiated tumor cells. Furthermore, cGAMP produced within irradiated tumor cells is transferred to the cytosol of DCs via gap junctions. Tumor-derived dsDNA or cGAMP activates cGAS–STING signaling and subsequent production type I IFNs within DCs as described above. DCs produce greater amounts type I IFNs compared to other cellular compartments in the TME. Type I IFNs are secreted and act on IFNAR receptors initiating a variety of responses including induction of IFN-stimulated genes, DC activation and maturation, as well as CD8+ T cell activation. Activated DCs cross-present TA on MHC I molecules which is recognized by tumor-reactive CD8+ T cells via their TCR. Activated CD8+ cytotoxic T cells recognize TA–MHC I complexes presented on the surface of target tumor cells and induce apoptosis through the release of perforin and granzyme B, or death receptor signaling involving FasL/FasR. Treatment with IR leads to the accumulation of TA-specific CD8+ T cells, specialized cross-presenting DCs, and type I IFNs within the TME—all of which are paramount for optimal antitumor immune responses induced by radiotherapy. Abbreviations: cytoplasmic chromatin fragments (CCFs); dendritic cells (DCs); double-stranded DNA (dsDNA); interferon (IFN); IFN-α/β-receptor (IFNAR); ionizing radiation (IR); mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA); T cell receptor (TCR); tumor-antigen (TA); tumor microenvironment (TME).