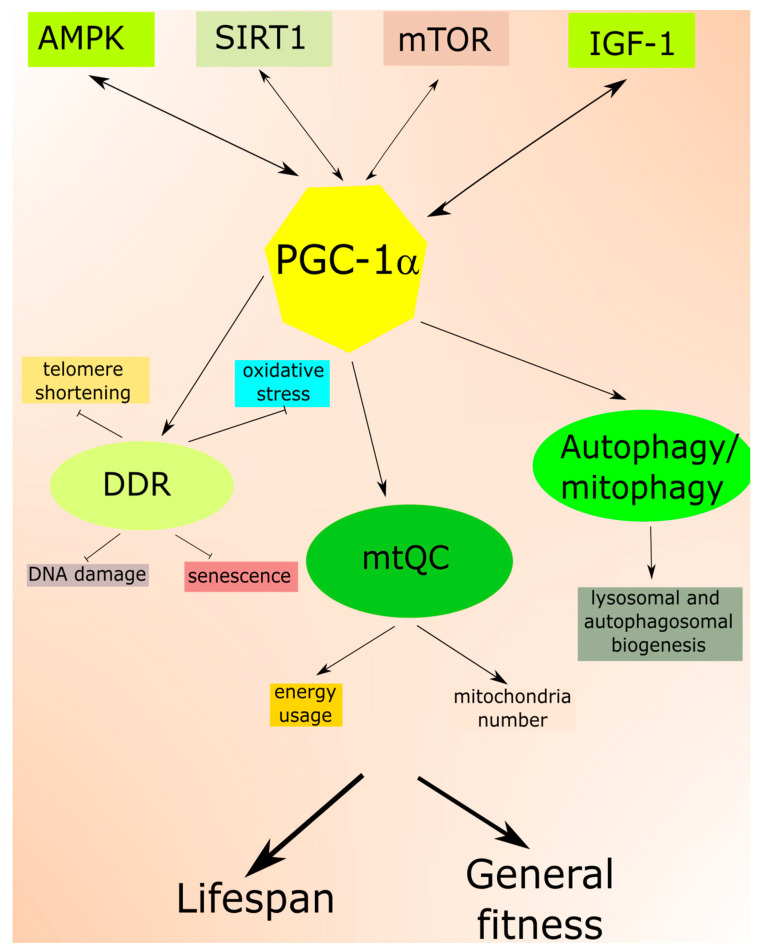
Figure 6.
The central role peroxisome proliferation-activated receptor coactivator 1 alpha (PGC-1α) in aging stress response. PGC-1α interacts with proteins playing an important role in aging regulation: 5’AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). These interactions result in the involvement of PGC-1α in the essential aging stress response pathways: DNA damage response (DDR), mitochondrial quality control (mtQC) and autophagy/mitophagy. PGC-1α is a primary regulator of antioxidant defense, and in this way, it can ameliorate DNA damage, telomere shortening and oxidative stress- and DNA damage-related senescence. PGC-1α controls mitochondrial response to stress associated with low energy allowing mitochondria to adjust their energy usage and number. PGC-1α may also contribute to the biogenesis of lysosomes and autophagosomes, essential for autophagy and mitophagy. These effects may extend lifespan and improve general fitness.