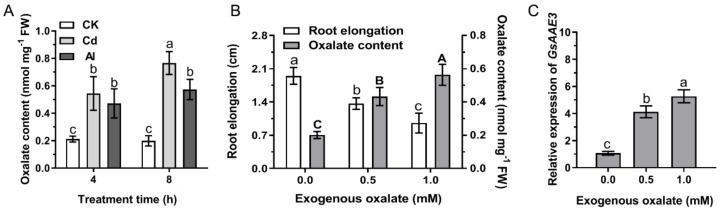
Figure 1.
The effect of Cd and Al stresses and exogenous oxalate on wild soybean (BW69) root tips. (A) Cd and Al stresses induced oxalate accumulation. The seedlings were exposed to nutrient solution containing 0 or 30 μM CdCl2 or AlCl3 for 4 or 8 h. (B) The effect of exogenous oxalate on wild soybean root elongation and oxalate content. The seedlings were exposed to 0, 0.5, 1.0 mM sodium oxalate for 24 h. Root elongation was measured with a ruler before and after treatment (n = 16). After treatment, the root tips (0–2 cm) were ground into fine powder with liquid nitrogen and then extracted with distilled water for oxalate content analysis (n = 3). The lowercase letters mean statistical significance of comparisons of root elongation data, and the uppercase letters mean statistical significance of comparisons of oxalate content data. (C) Correlation between oxalate content and GsAAE3 expression (n = 3). The expression of GsAAE3 was determined by qRT-PCR. All data are presented as means ± SD. Different letters indicate statistically significant difference, using one-way ANOVA and Duncan’s test (p ≤ 0.05).