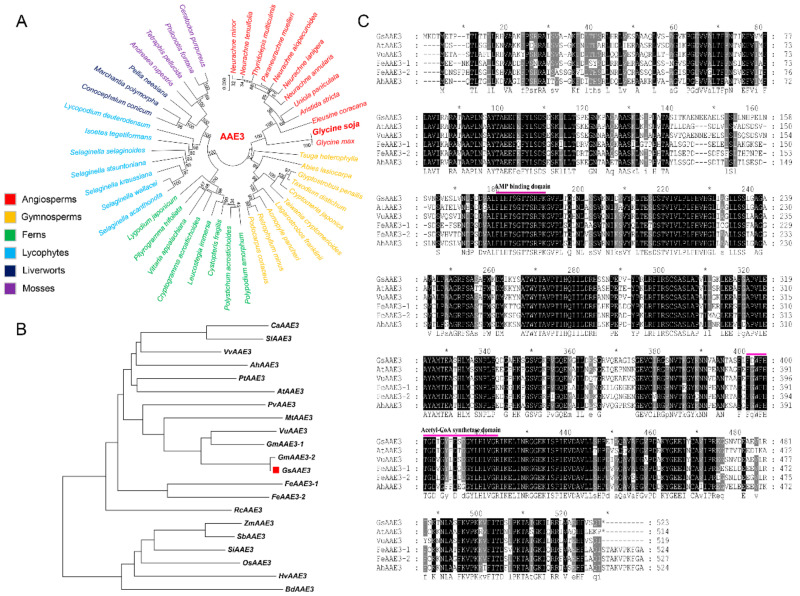
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic analysis and multiple sequence alignment. (A) Phylogenetic trees of AAE3 proteins in representative species of major lineage of plants (sequences of representative species can be found in https://db.cngb.org/onekp/, accessed on 18 November 2020). Clades are indicated by different colors. (B) Phylogenetic analysis of AAE3 proteins in higher plants. All the available amino acid sequences and the accession numbers of AAE3 proteins were obtained from the NCBI databases (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 20 October 2020). The AAE3 proteins including Capsicum annuum (CaAAE3; NP_001311686), Solanum lycopersicum (SlAAE3; XP_004234395), Vitis vinifera (VvAAE3; XP_002267459.1), Amaranthus hypochondriacus (AhAAE3), Populus trichocarpa (PtAAE3; XP_002322473), Arabidopsis thaliana (AtAAE3; AT3G48990), Phaseolus vulgaris (PvAAE3; XP_007143422), Medicago truncatula (MtAAE3; XP_003599555), Vigna umbellate (VuAAE3; KX354978), Glycine max (GmAAE3-1; XP_003534000.1, GmAAE3-2; XP_014619651.1), Glycine soja (GsAAE3; BW679327.1), Fagopyrum esculentum (FeAAE3-1 and FeAAE3-2), Ricinus communis (RcAAE3; XP_0002509782), Zea mays (ZmAAE3; AEY64280), Sorghum bicolor (SbAAE3; KXG27467), Setaria italic (SiAAE3; XP_004960018), Oryza sativa (OsAAE3; Os04g0683700), Hordeum vulgare (HvAAE3; BAK00674), and Brachypodium distachyon (BdAAE3; XP_003579506). (C) Multiple sequence alignment of AAE3 proteins from Glycine soja (GsAAE3), Vigna umbellate (VuAAE3), Arabidopsis thaliana (AtAAE3), Medicago truncatula (MtAAE3), Amaranthus hypochondriacus (AhAAE3), and Fagopyrum esculentum (FeAAE3-1 and FeAAE3-2). The conserved AMP binding domain and acetyl-CoA synthetase domain are indicated.