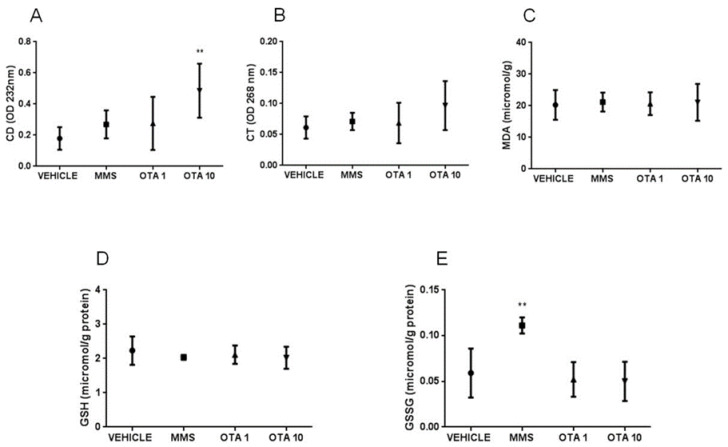
Figure 4.
The effect of repeated daily oral dose (72 h) OTA exposition on some lipid peroxidation parameters and reduced and oxidized glutathione concentration in the kidney cortex. A: Levels of conjugated dienes (CD) in kidney samples in case of repeated daily oral dose (72 h) OTA treatment. The highest OTA dose increased significantly (p < 0.01) the level of conjugated dienes in the kidney. B: Levels of conjugated trienes (CT) in kidney samples in case of repeated daily oral dose (72 h) OTA treatment. The applied OTA doses did not cause significant alterations. C: Malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration in kidney samples in case of repeated daily oral dose (72 h) OTA treatment. The applied OTA doses did not cause significant changes. D: Reduced glutathione (GSH) concentration in kidney samples in case of repeated daily oral dose (72 h) OTA treatment. The applied OTA doses did not cause significant alterations. E: Oxidized glutathione (GSSG) concentration in kidney samples in case of repeated daily oral dose (72 h) OTA treatment. The applied OTA doses did not significantly alter, while the MMS treatment increased the GSSG concentration significantly (p < 0.01). Abbreviations: MMS: methyl-methanesulfonate-treated group; OTA 1 and OTA 10: 1 and 10 mg/kg bw ochratoxin-A-treated groups. Mean ± S.D. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test. ** p < 0.01 vs. vehicle.