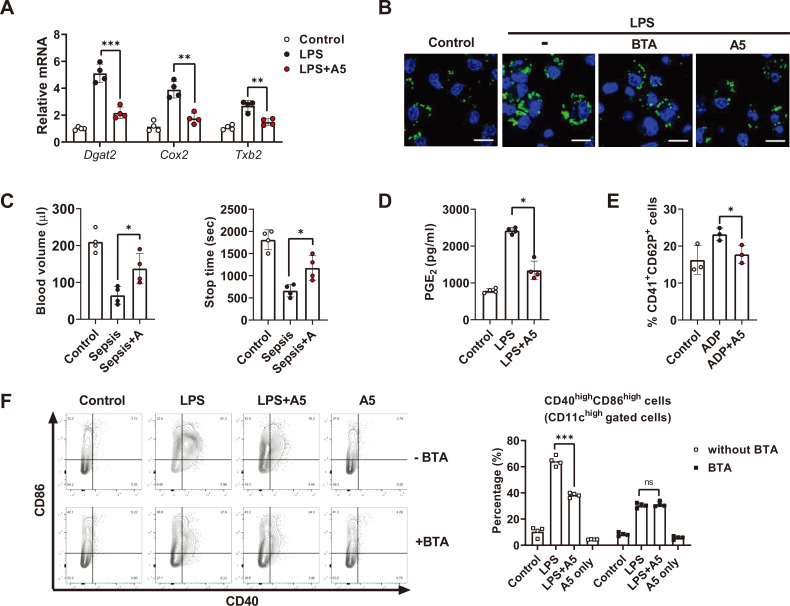
Fig. 5. Allithiamine inhibits “citrate–lipid droplet” pathway and exerts anticoagulant effect during endotoxemia.
(A, B, and D) BMDCs were activated with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 16 h in the presence of allithiamine at a concentration of 5 µM. (A) Relative mRNA levels were calculated. (B) Lipid droplet formation in dendritic cells was measured by confocal microscopy using BODIPY 493/503. Scale bar = 10 µm. (C) Tail bleeding assay was performed in LPS-induced model comparing control with allithiamine injection group. Twelve hours after LPS injection, the tail tip was amputated, and the volume of blood flowing out of the tail and the total bleeding time were estimated. (D) Supernatants were collected, and PGE2 concentration was assessed using ELISA. (E) Platelets were isolated from C57BL6 mice, activated with ADP 2 mM, and treated with or without allithiamine at 5 µM. CD41+ and CD62P+ cells were detected by flow cytometry. (F) CD11c+CD86+ CD40+ cells during LPS-induced activation with or without BTA 5 µM or allithiamine 5 µM were detected by flow cytometry. Asterisk indicates significant differences (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001) from data obtained during the LPS-only challenge. ns, not significant. Allithiamine is designated as A.