Fig 3.
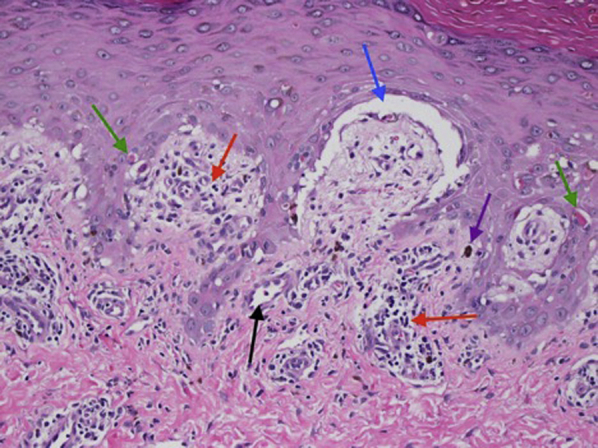
A biopsy of a hemorrhagic blister shows a subepidermal vesicle (blue arrow) on a background of an interface inflammatory reaction (red arrows) with dyskeratotic keratinocytes (green arrows), pigment incontinence (purple arrow), and superficial perivascular lymphocytic inflammation (black arrow). There was no significant thickening or hyalinization of the dermal blood vessel wall. Mucin deposition is not visualized (hematoxylin-eosin stain; ×200).
