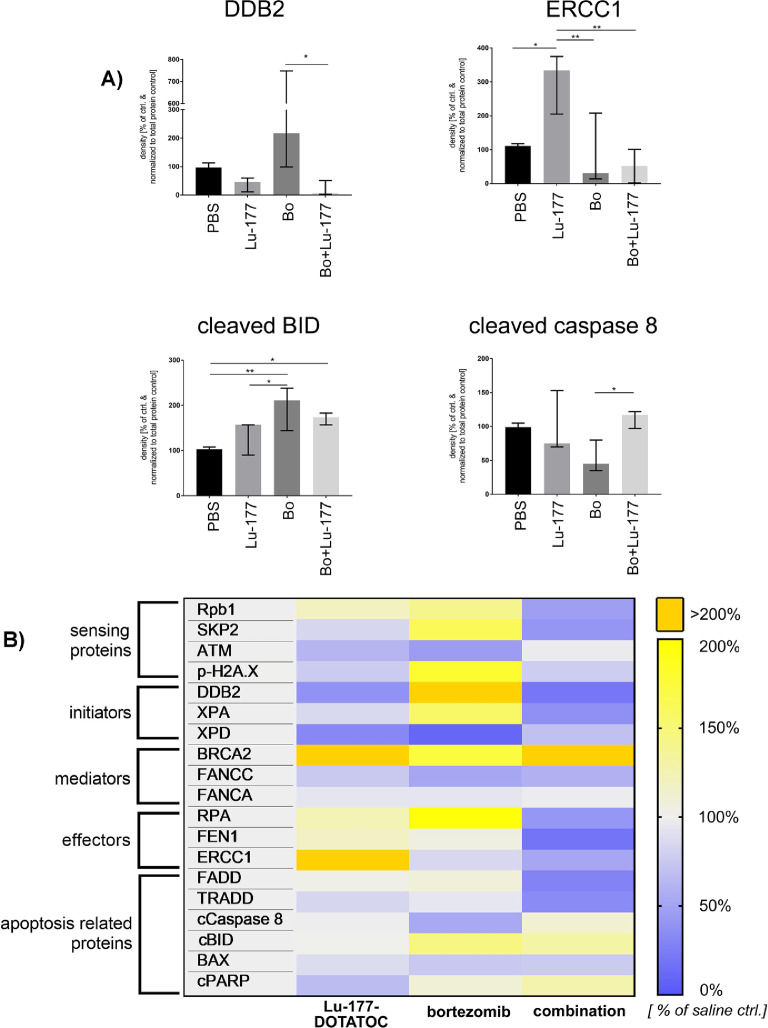
Figure 5.
Regulation of DNA damage repair related proteins after bortezomib-combined PRRT in vivo: Chicken CAM xenografted tumors were treated i.v. with a single dose of ∼20 MBq 177-Lu-DOTATOC with and without 25 nM bortezomib versus saline control and explanted 6 d after treatment. Protein abundance of proteins involved in the sensing of DNA damage, initiation, signal transduction and execution of DNA repair and apoptosis was analyzed by western blot and densitometry was performed using Image J v1.53. Data was normalized to densitometric data of total protein stain (ponceau S). (A, B) We identified significant protein expression alterations in the combined treatment groups for DDB2, ERCC1, cleaved BID and p38, p41/p43 cleaved caspase 8 (Fisher's Least Significant Difference Test) and an overall downregulation of DNA repair-related genes, especially of the BER pathway (RNA polymerase II, DDB2, XPD, XPA, RPA, ERCC1, FEN1). (B) Heatmap shows mean of ≥3 independent experiments per treatment group normalized to total protein stain and relative to saline control. Raw data is shown in Supplementary Figure 4. BER, Base Excision Repair,; Bo, bortezomib; Lu-177, Lu-177-DOTATOC; Rpb1, RNA polymerase II subunit B1 c-terminal domain, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.