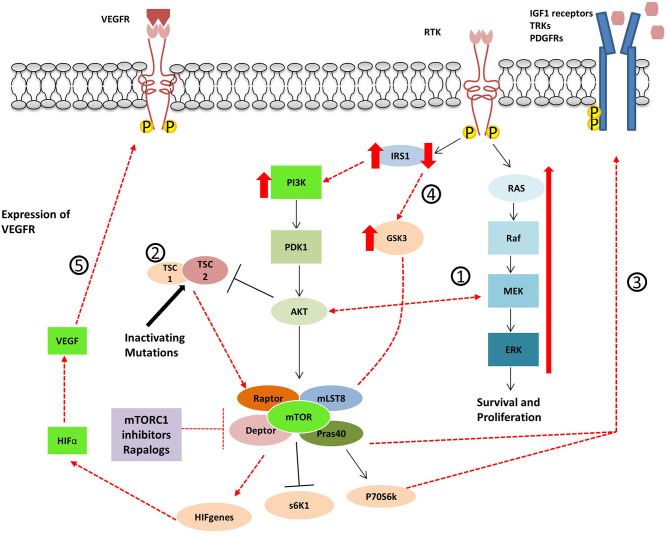
Figure 4.
Proposed mechanisms for resistance to Rapalogues in NET. 1- Inhibition of mTOR results in PI3k-Akt-mTOR pathway reactivation and MAPK pathway activation. 2- Inactivating mutations in TSC1/2 cause the inactivation of the TSC1/TSC2 protein complex leading to mTOR hyperactivation. 3- mTOR inhibitor treatment cause an increase in tyrosine kinase receptors and growth factor secretion. 4- GSK3 over-expression accompanied by the decrease of IRS-1 protein leads to decreased autophagy and cell resistance to Everolimus. 5- The up-regulation of angiogenic factors mTOR-independent or the re-expression of HIFα.