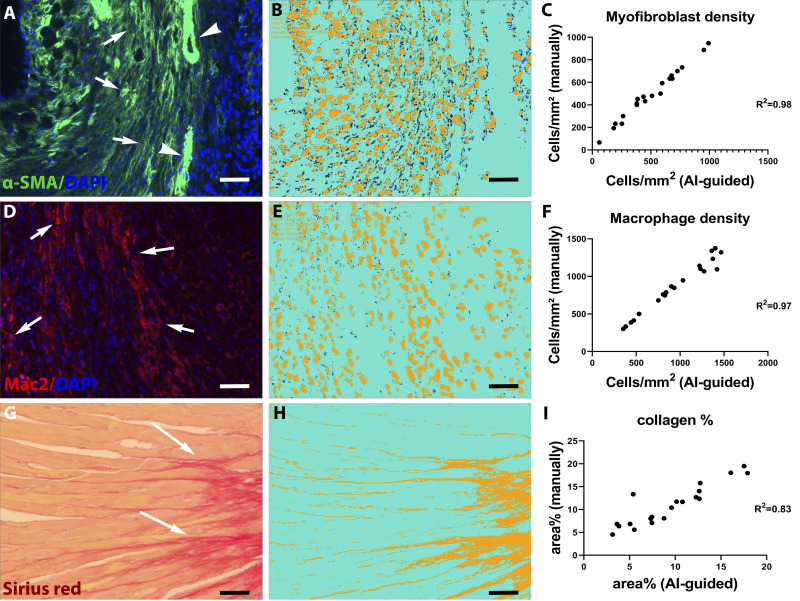
Fig. 1.
Validation of artificial intelligence (AI)-based quantification protocols of myofibroblast density, macrophage density, and collagen content. A–C: α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) immunofluorescence was used to identify myofibroblasts as spindle-shaped immunoreactive cells located outside the vascular media (A, arrows). Arrowheads show vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). The Intellesis Trainable Segmentation module of Zen 2.6 Pro software (Carl Zeiss Microscopy, New York, NY), an AI-based model, was trained on multiple fields of different regions of the myocardium to segment the images and identify myofibroblasts. Objects of interest were defined as the DAPI-α-SMA double-positive profiles, excluding VSMCs. B: unstained myocardium (including VSMCs) was considered the background. The trained AI-based model exhibited excellent correlation with manual measurement of myofibroblast density in the same fields (r = 0.98, P < 0.0001, n = 20). D–F: Mac2 immunofluorescence was used to identify macrophages (arrows). The AI-based quantification model was validated, showing excellent correlation with manual counts (r = 0.97, P < 0.0001, n = 20). G–I: Picrosirius red staining was used to label collagen fibers. The AI-based quantification model showed excellent correlation with manual quantification of collagen content (r = 0.83, P < 0.0001, n = 20). Scale bar, 20 μm.