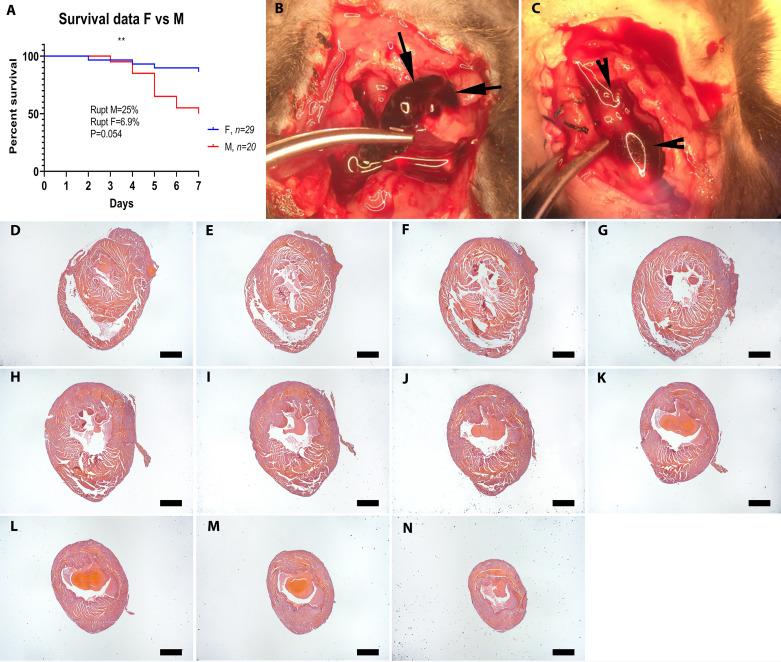
Fig. 2.
Sex-specific mortality in infarcted mice and use of visual inspection vs. systematic histological analysis to identify the cause of death. A: when compared with female (F) C57BL/6J mice, male (M) animals had significantly higher post-myocardial infarction (MI) mortality (**P < 0.009), and a trend toward increased cardiac rupture rates (P = 0.054, n = 29 F, 20 M). To identify rupture-related deaths, visual inspection criteria were used. Criteria for rupture included a blood clot or blood in the chest (hemothorax; B and C, arrows) or presence of a cardiac rupture site. D–N: systematic histological analysis was performed by sectioning the entire heart from base to apex at 300-mm partitions and staining the first section of each partition (D–N shows consecutive myocardial sections used to systematically study the cause the death. Scale bar, 1 mm.