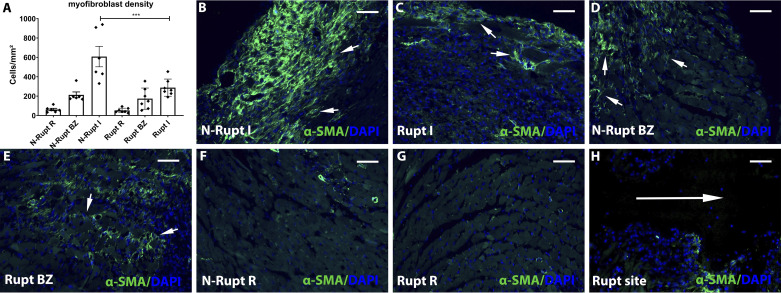
Fig. 5.
Rupture is associated with attenuated myofibroblast infiltration in the healing infarct. A: artificial intelligence (AI)-based quantitative analysis showed that mice dying of cardiac rupture had markedly lower myofibroblast density in the infarcted myocardium (I) compared with mice dying the absence of rupture (***P < 0.0001, n = 6–7/group). No significant differences were noted in the border zone (BZ) and in the remote remodeling myocardium (R). B–H: representative images show identification of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) + myofibroblasts in infarcted hearts (short arrows). Infarcted segments in mice dying of rupture (C) have attenuated myofibroblast infiltration. H: please note the absence of myofibroblasts in the rupture site (long arrow). Time points studied histologically were comparable between groups, as there was no significant difference in the time of death (rupture group: 5.0 ± 0.53 days, n = 7; no rupture group: 5.16 ± 0.4, n = 6). Scale bar, 50 μm.