Figure 1. Multi-omics workflow.
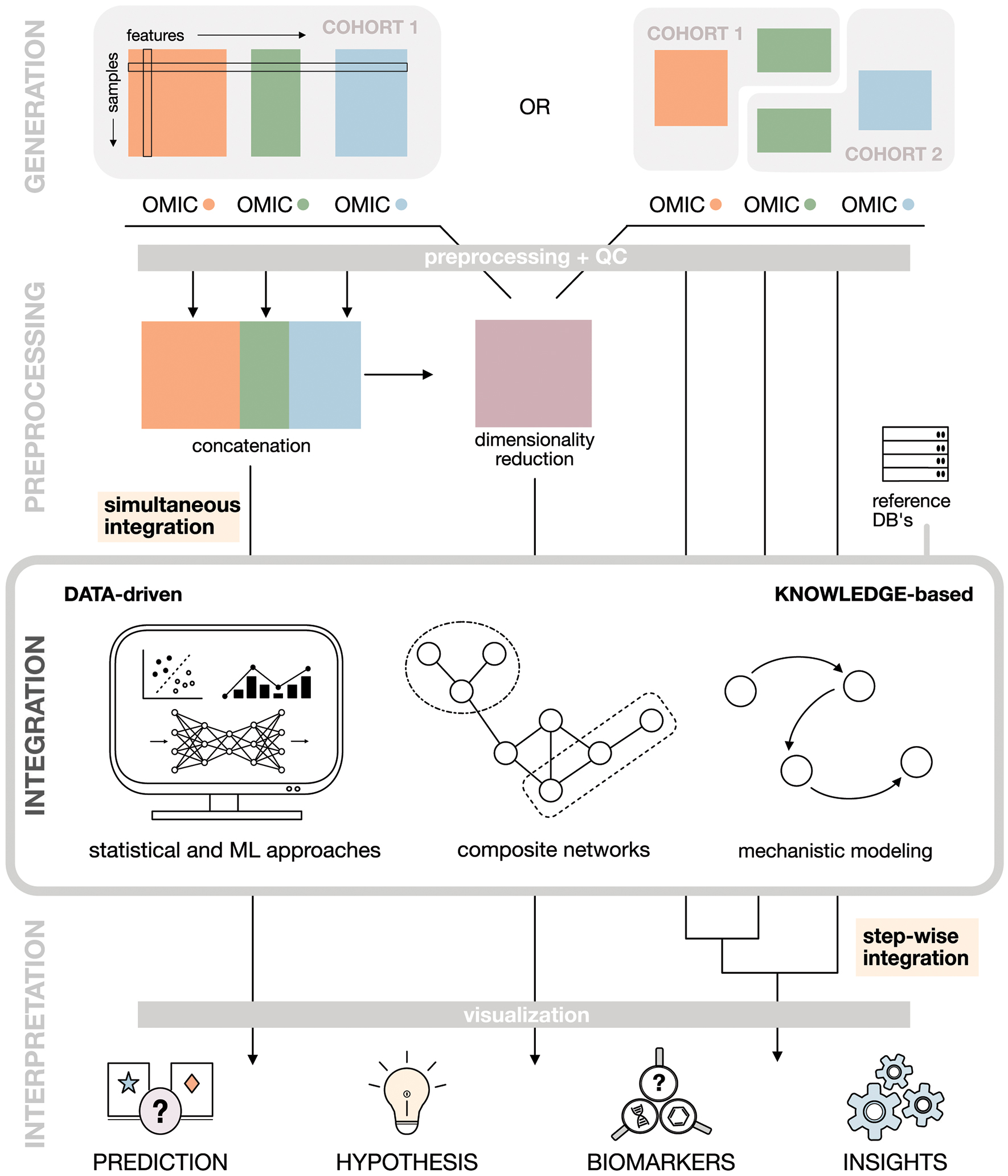
A typical multi-omics analysis can generally be broken down into 4 steps. (i) Data generation. Study design, sample preparation and subsequent data acquisition through high-throughput analytical platforms lead to different data scenarios. (ii) Data preprocessing and dimensionality reduction. Raw data collected on different omics layers is preprocessed appropriately and dimensionality reduction can be applied to reduce the number of variables (measured biological entities). (iii) Data integration. Data from different omics layers are analyzed and integrated using data-driven, knowledge-based or hybrid integration approaches. The choice of method depends on the input data and research question of interest. (iv) Data interpretation. Post-integration visualization and analysis of the integration results (e.g., statistical model or network) can identify novel biomarker candidates, generate testable hypothesis or reveal meaningful biological relationships.
