FIGURE 1.
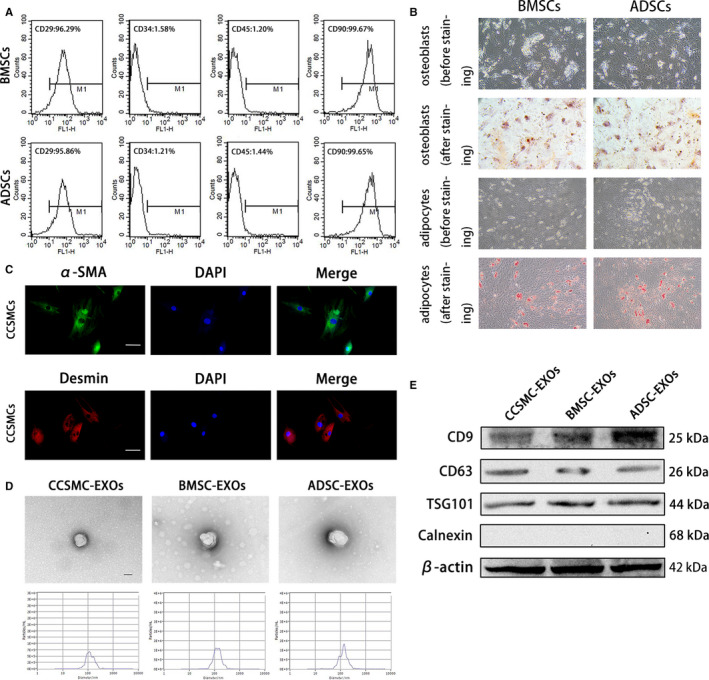
Cell identification and exosome characterization. (A) Representative flow cytometry histograms of BMSCs and ADSCs show positive staining for CD29 and CD90 but not for CD34 and CD45. (B) BMSCs and ADSCs were successfully induced into osteoblasts (positively stained with Alizarin Red S) and adipocytes (positively stained with Oil Red O). The magnification is 100×. (C) Representative immunofluorescence results of CCSMCs show positive expression for α‐SMA and desmin. Scale bars = 50 μm. (D) Exosomes derived from CCSMCs, BMSCs and ADSCs were observed using transmission electron microscopy, and the particle size distributions of the exosomes were measured by nanoparticle tracking analysis. Scale bars = 100 nm. (E) Representative results of Western blot analysis of exosomes derived from CCSMCs, BMSCs and ADSCs show positive expression for CD9, CD63 and TSG101 but not for calnexin. CCSMC: corpus cavernosum smooth muscle cell; BMSC: bone marrow stem cell; ADSC: adipose‐derived stem cell; CCSMC‐EXOs: exosomes derived from corpus cavernosum smooth muscle cells; BMSC‐EXOs: exosomes derived from bone marrow stem cells; ADSC‐EXOs: exosomes derived from adipose‐derived stem cells; α‐SMA: α‐smooth muscle actin; DAPI: 4’,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole
