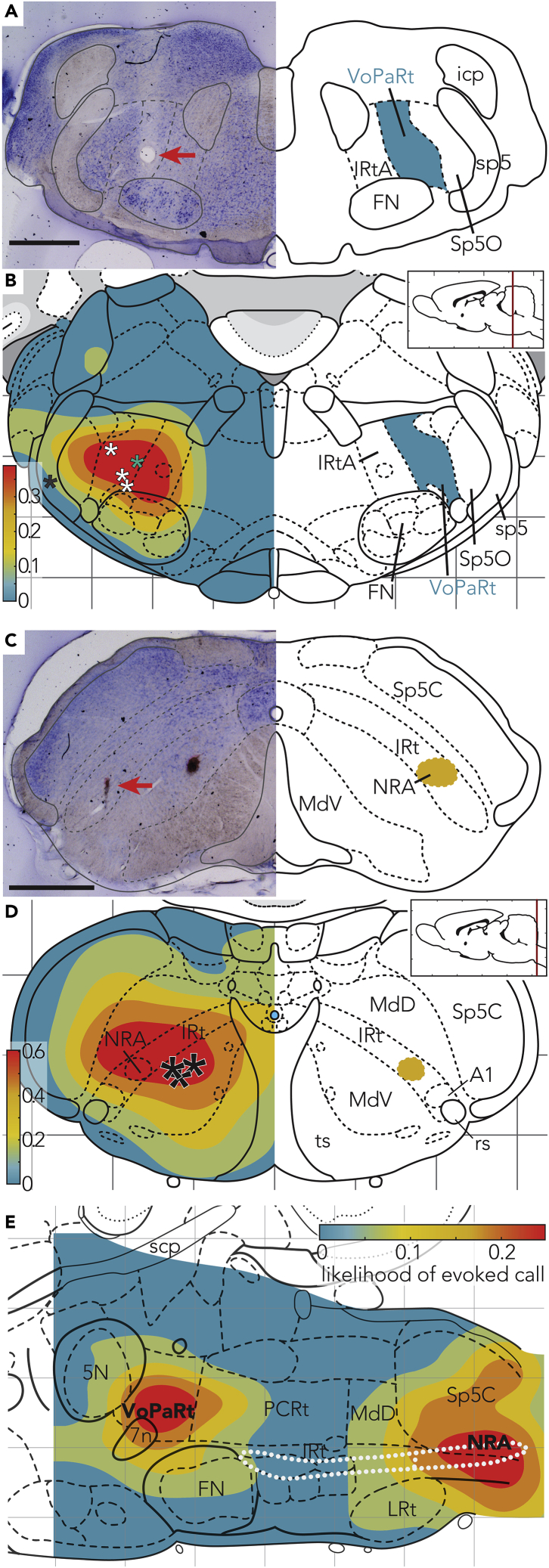
Figure 3.
The Anterior Region of the VPG Corresponds to the Parvicellular Reticular Formation that We Term the VoPaRt, whereas the Posterior Region Maps to the NRA and Its Close Surrounding
(A) Coronal section with Nissl staining. Lesion (red arrow) in the anterior part, −10.80 mm from bregma. Scale bar, 1 mm. On the right, identified regions are drawn.
(B) Coronal map of the average vocalization rate as response of brainstem stimulation. Asterisks indicate lesions placed at sites of strongest responses across animals (single black asterisk indicates a lesion placed 1 mm lateral of the strongest response). In the anterior-posterior axis, lesions ranged from bregma −10.50 mm to bregma −11.16 mm. Lesions have been overlayed with the coronal section of bregma −10.80 from Paxinos & Watson Rat Brain Atlas for illustration purposes.
(C) Coronal section with Nissl staining. Lesion (red arrow) in the posterior part −14.52 mm from bregma. Scale bar, 1 mm.
(D) Average depth response rate to brainstem stimulation superimposed with the Paxinos brain atlas −15.00 mm posterior of bregma. Lesions ranged from −14.52 to −15.72 mm posterior of bregma.
(E) Parasagittal view of the brainstem with a heatmap showing sites of calls evoked by electrical stimulation. The white, dotted structure shows the nucleus ambiguous and the nucleus retroambiguus (subsection in posterior brainstem).
5N, motor trigeminal nucleus; 7n, facial nerve; A1, A1 noadrenaline cells; FN, facial nucleus; icp, inferior cerebellar pedunculus; IRtA, intermediate reticular nucleus alpha part; IRt, intermediate reticular nucleus; LRt, Lateral reticular nucleus; MdD, medullary reticular nucleus dorsal part; MdV, medullary reticular nucleus ventral part; rs, rubospinal tract; Sp5C, Spinal trigeminal tract caudal part; Sp5O,Spinal trigeminal tract oral part; sp5, spinal trigeminal tract; soc, superior olivary complex; ts, tectospinal tract.