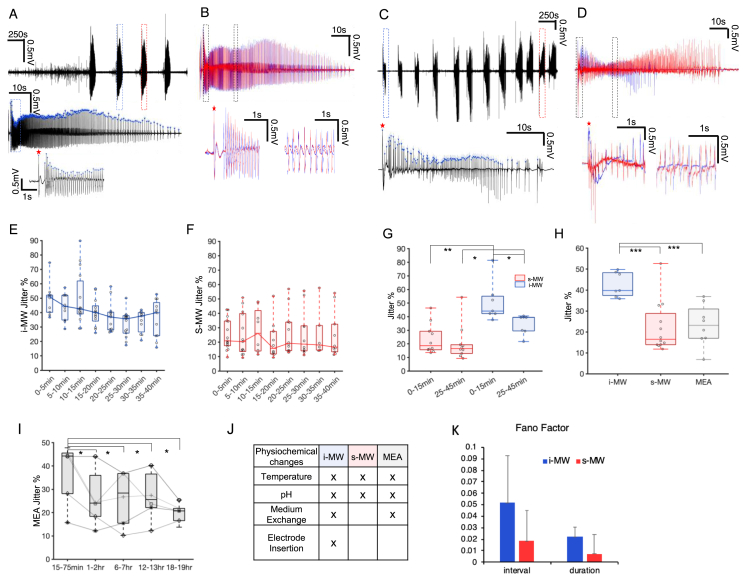
Figure 2.
Average jitter percentage calculation and comparison among three recording systems. A, C Examples of recording from s-MW and i-MW respectively are presented in black trace. Zoomed-in window of a single ictal event which is indicated by blue dashed box is provided at the bottom for both examples. B, D Two ictal events that are specified by blue and red dashed boxes in A and C respectively are overlaid according to the alignment spike (red and blue trace). Two zoomed-in time windows at different time points of the recording are presented at the bottom of these two traces for both s-MW and i-MW (indicated by dashed boxes). Blue arrows indicate the spikes and red star specifies the alignment time point. Jitter between two selected events in B and D are 11% (low jitter) and 61% (high jitter), respectively. E, F Jitter evolutions within 1 h time window of recordings from i-MW and s-MW are illustrated in box plots. Values of jitter are binned into 5 min intervals. The whiskers represent the range of the data. The 25th and 75th percentiles of the samples are contained within the top and bottom of the boxes. The line in the middle represent the median. G Jitter at the first 15 min and the last 15–20 min of the recordings are averaged and compared through paired t-test both for s-MW and i-MW samples. The initial and last 15–20 min then compared between two recording modalities through student t-test (p-value ∗ = 0.01, p-value ∗∗ = 0.001, n = 7 recordings, 7 slices for i-MW, and n = 10 recordings, 5 slices for s-MW). H Average jitter percentages were compared among three devices during the more stabilized period and after first 15 min of the recording. The highest value was obtained from i-MW (Student t-test, p-value ∗ <0.04, p-value ∗∗ = 0.001, n = 8 recordings, 5 slices from MEA device, n = 7 recordings, 7 slices from i-MW setting, and n = 12 recordings, 5 slices from s-MW setup). I Average percentage of jitters are calculated within a 1 h time window after 15 min, 1, 6, 12, and 18 h of media exchange. Student t-test was applied to the jitter values of different time points post media exchange. Average jitter percentage is significantly higher during the 1 h time window after 15 min post media changing compared to the other time points (p-value ∗ <0.05, n = 5 slices). J The table summarizes the external disturbances that are present for all three recording platforms. K Duration and interval of seizure-like activities measured from the recordings and normalized fano factors (ratio of variance over mean) are compared between i-MW and s-MW platforms. Fano factors of seizure durations are significantly higher from i-MW recordings (student t-test, p-value < 0.05).