Figure 3.
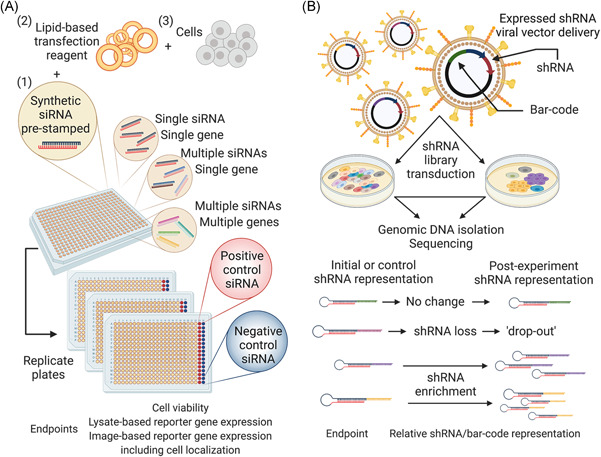
RNAi screening strategies. (A) A diagrammatic representation of plate‐based arrayed siRNA screening strategies compatible with endpoints such as cell viability, and luminescence or fluorescence reporter assays. Synthetic siRNAs are pre‐stamped into each well of a multi‐well plate (1), and the siRNA–liposome complex formed by adding a pre‐optimized amount of a lipid‐based transfection reagent (2). Following the addition of cells (3) to the siRNA–liposome complex, the transfected cells grow for 24–96 h under standard cell culture conditions before assessing a relevant endpoint. (B) A simplified outline of bar‐coded shRNA‐based pooled screening using a lentiviral vector delivery system. Cell populations transduced using pooled libraries that retain a normalized representation of each shRNA form the basis of different experimental groups, for example, different time‐points, Day 0 and Day 21, or two treatment conditions, vehicle or active compound. Following a selection period, the isolation of genomic DNA from each cell population allows for the assessment of the relative representation of each shRNA. RNAi, RNA interference; shRNA, short hairpin RNA; siRNA, small interfering RNA
