Fig. 2.
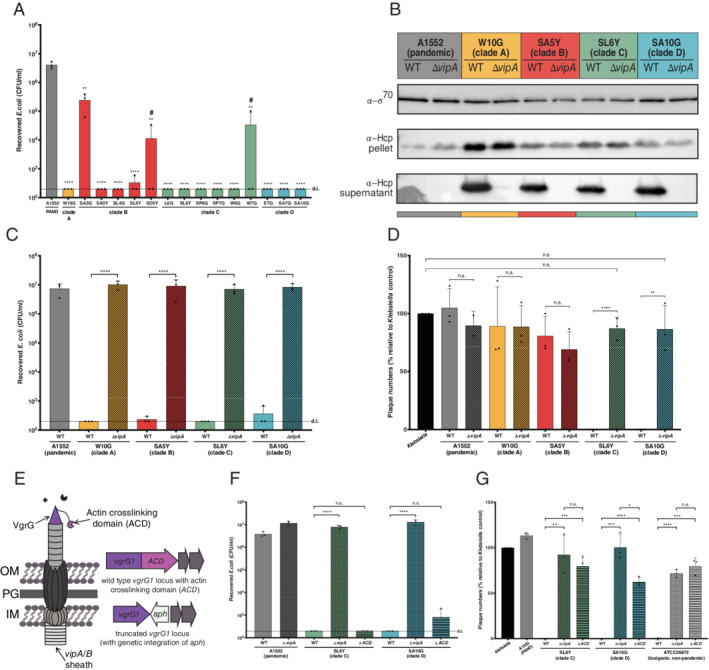
Constitutive T6SS activity linked to an ACD‐containing effector inhibits amoebal grazing.
A, C, F. Bacterial killing assays using E. coli as prey. Numbers of surviving prey are depicted on the Y‐axis (CFU ml−1). Statistical significance in panel A is shown above each strains' bar and calculated relative to the T6SS‐silent negative control strain A1552. #, for these strains, the killing activity was only reduced in one of the three independent experiments.
B. T6SS activity in representative environmental strains. Hcp detection in WT and ΔvipA mutants of representative environmental isolates. Intracellular (pellet) and secreted (supernatant) Hcp were assessed by immunoblotting using Hcp‐directed antibodies. Detection of σ70 served as a loading control.
D, G. T6SS‐ and ACD‐dependency of the anti‐amoebal defence. Plaque formation by D. discoideum on bacterial lawns formed by representative V. cholerae WT, ΔvipA derivatives (D and G) and ACD‐minus (G) strains. Details as in Fig. 1. The toxigenic non‐pandemic strain ATCC25872 and its site‐directed mutants served as control in panel G.
E. Simplified scheme of the T6SS. The actin cross‐linking domain (ACD) consists of a C‐terminal extension of the VgrG1 tip protein and this multidomain protein is encoded by the vgrG1 locus (shown on the right). Removal of the ACD‐encoding sequence was accomplished through site‐directed integration of a stop codon concomitantly with an aph selective marker. Bar plots in all panels represent the average of at least three independent biological replicates (±SD). d.l., detection limit. Statistical significance is indicated (n.s., not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; for panel A, each sample was compared to the A1552 control).
