Fig. 3.
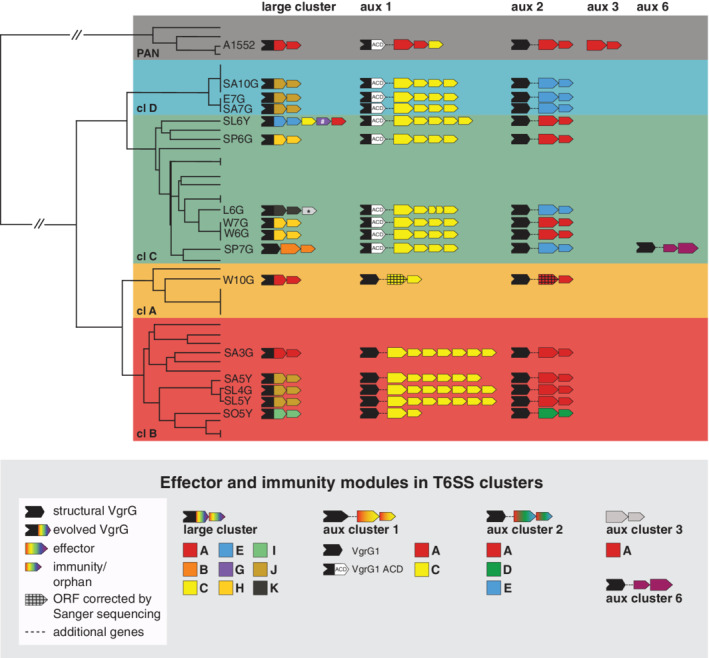
T6SS effector/immunity typing scheme of pandemic and environmental V. cholerae. The previously published phylogenetic tree was freely adapted from Keymer et al. 2007 (not fully to scale). The clade colour code is depicted in the background. The E/I type of each T6SS cluster (large cluster as well as auxiliary (aux) clusters 1, 2, 3 and 6) are schematized for each strain. Large black arrows symbolize vgrG genes, which were classified as structural (black) or evolved (coloured tips, to represent the different types of C‐terminal effector domains). Large and small coloured arrows represent effector and immunity genes, respectively, according to the colour code indicated in the legend below the scheme. Immunity genes that are not adjacent to a putative effector gene are considered as orphan immunity loci. * depicts an orphan immunity gene from strain L6G whose gene product was slightly below the amino acid identity threshold of 30% (20.3%) relative to C‐type immunity proteins. # depicts an orphan immunity gene that is a homolog to bona fide immunity genes in other genomes. Effector genes in auxiliary clusters 1 and 2 of strain W10G (marked in figure with a pattern) were wrongly annotated in the PacBio genome sequence (containing several stop codons) due to a frameshift sequencing artefact; this sequencing error was corrected by Sanger sequencing.
