Figure 1.
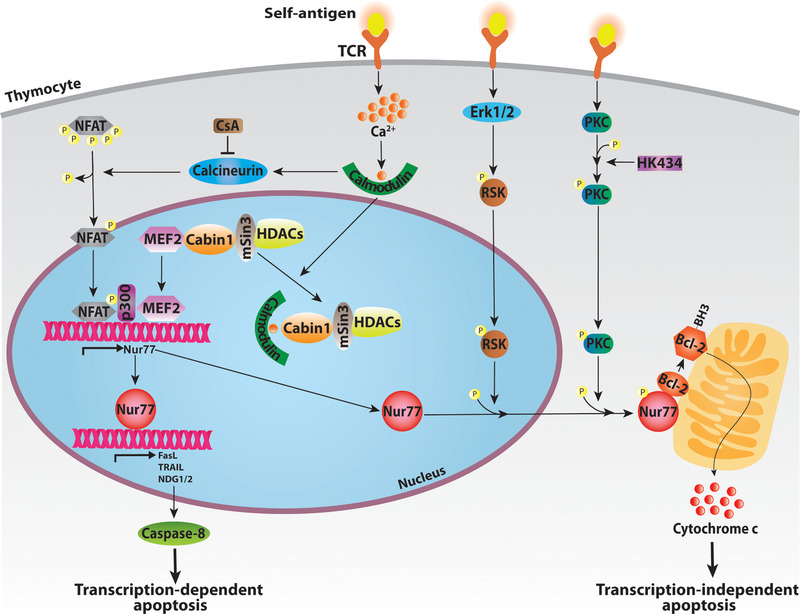
Regulation of Nur77 expression and activation of downstream pathways in thymocytes. TCR stimulation by self‐ligand binding increases intracellular calcium (Ca2+). Calcium activates calmodulin, which regulates Nur77 transcription in distinct ways. Calmodulin can form a complex with calcineurin, dephosphorylating nuclear factor of activated T‐cells (NFAT). NFAT then translocates to the nucleus, where it binds MEF2, enhancing its affinity for co‐activator p300, inducing Nur77 transcription. Alternatively, calmodulin releases MEF2 from Cabin1 by competitive binding. Once Nur77 is expressed it can directly bind promoters of its target genes, activating the transcription‐dependent apoptosis program. To activate transcription‐independent pathways, ERK1/2 and PKC are required, inducing translocation of Nur77 from the nucleus to mitochondria (involving protein phosphorylation). There, Nur77 interacts with Bcl‐2 proteins, exposing their BH3‐domain, inducing cytochrome c mediated organelle dysfunction and apoptosis.
