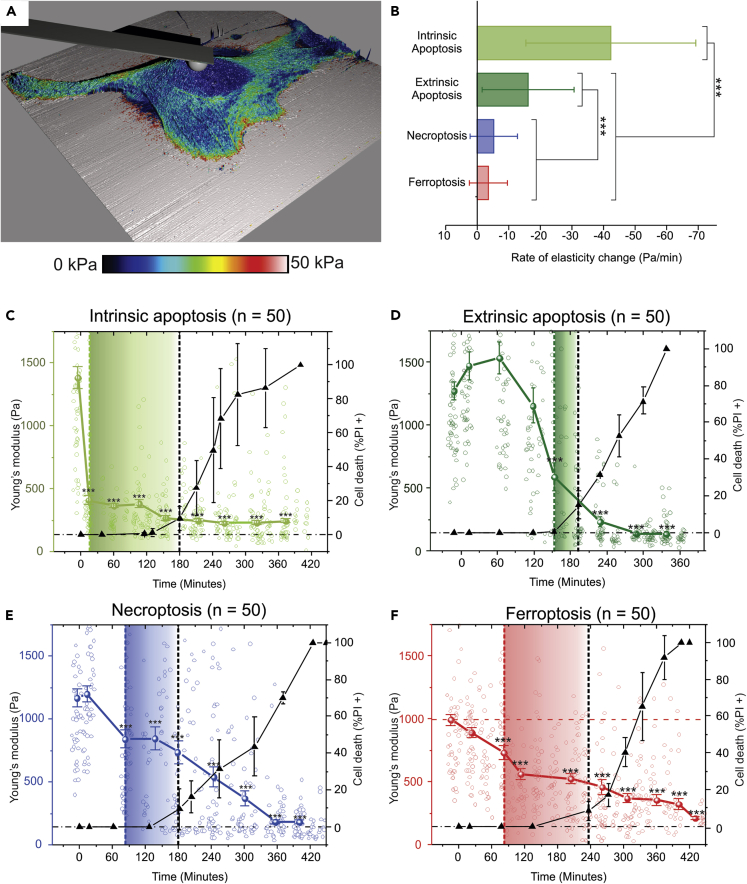
Figure 3.
AFM Mechano-Biology Analysis of the Elasticity Dynamics of Cells Undergoing RCD Modalities
(A) A single-cell high-resolution elasticity analysis indicating the uniform elasticity distribution in the nuclear area (i.e., the blue area indicated by the cantilever immobilized spherical colloidal probe).
(B) Bar graph indicating the maximum decrease rates during the process of each RCD modality. For both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis, a significantly higher decrease rate is observed compared with the other modalities (p values are provided in Table S2). The error bars in the right y axis of the graph indicate the standard deviation.
(C–F) The time dependence of the elasticity of cells undergoing intrinsic apoptotic, extrinsic apoptotic, necroptotic, and ferroptotic RCDs, respectively: left y axis and the colored line indicate elasticity values, right y axis and black line indicate a late stage of cell death determined by the PI status (expressed as the percentage of the measured cells), shaded rectangles indicate the delay between the first significant difference in elasticity compared with the first cell death signal (PI+). (C) Intrinsic apoptosis is characterized by a steep elasticity drop at the frist timepoint of measuring, detection with fluoresence lags behind significantly (166 minutes). (D) Extrinsic apoptosis shows an initial elasticity increase which is followed by a steep elasticity decrease, first detection with fluoresence lags behind 40 minutes. (E) Elasticity decreases gradually during necroptosis, a significant decrease of elasticty can be discerned 99 minutes before the first fluorescent signal appears. (F) Ferroptosis is characterized by a gradual elasticity decrease over time of the cell death process, significant elasticity decrease precedes the fluorescent signal by 155 minutes. The error bars in the left y axis graphs indicate the standard error of means (SEM) n = 50. Errorbars for the data on the right y-axis represent the standard deviation. (The statistical analysis was determined by a Kruskal-Wallis test followed by a pairwise Wilcoxon test with Benjamini-Hochberg adjusted p values, ∗∗∗p < 0.001; n = 50). See also Figure S3 and Tables S1–S3.