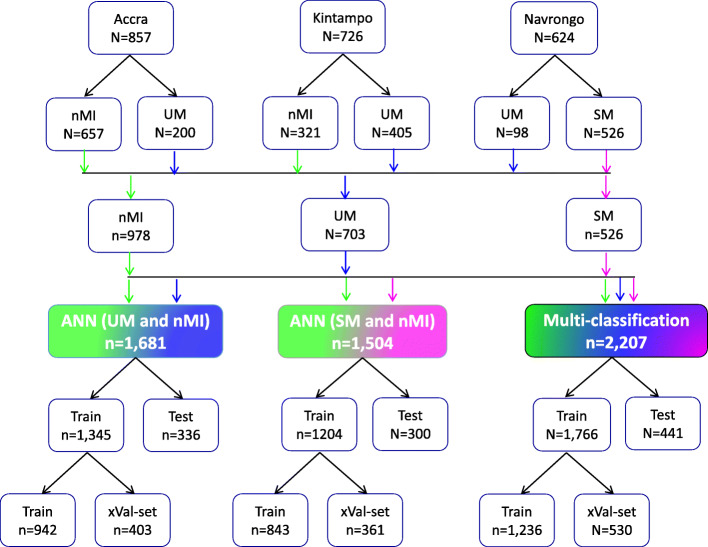
Fig. 1.
Study population and data splitting for building the ANN for clinical malaria. Samples were collected from one low transmission area (Accra, n = 857) and two high transmission areas: Kintampo (n = 726) and Navrongo (n = 624). The nMI (n = 978) were collected from Kintampo and Accra and UM (n = 703) were collected from all three areas, while the SM (n = 526) samples were collected from Navrongo. A multi-classification ANN model was developed for nMI, UM, and SM, which was further evaluated by binary ANN models (1) ANN (UM vs nMI) and (2) ANN (SM vs nMI). For each model, data splitting was achieved by dividing data in an 80:20% ratio into training (Train) and testing (Test). The 80% training data was further split into a 70:30% ratio for training (Train) and cross-validation (xVal-set)