Figure 3.
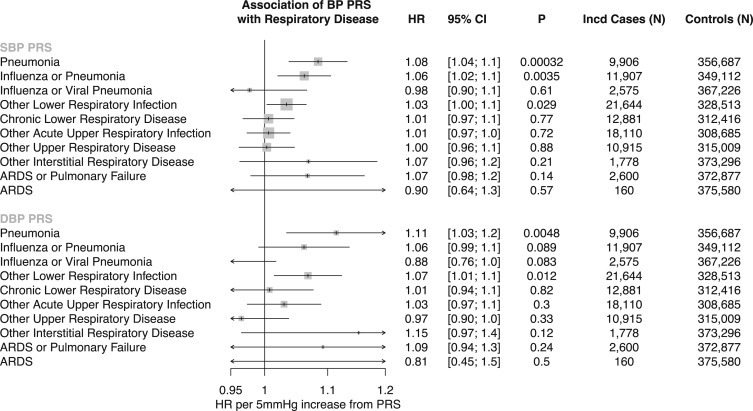
Genetic Association of Blood Pressure with Incident Respiratory Disease
Association of SBP PRS and DBP PRS with incident respiratory diseases (defined in Table S2), adjusted for age, age2, sex, smoking status, and the first ten principal components of population stratification in the UK Biobank. Effects are interpreted as HR per 5 mm Hg increase from the respective PRS. HR and 95% CI are displayed. SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; PRS, polygenic risk score; HR, hazard ratio.
