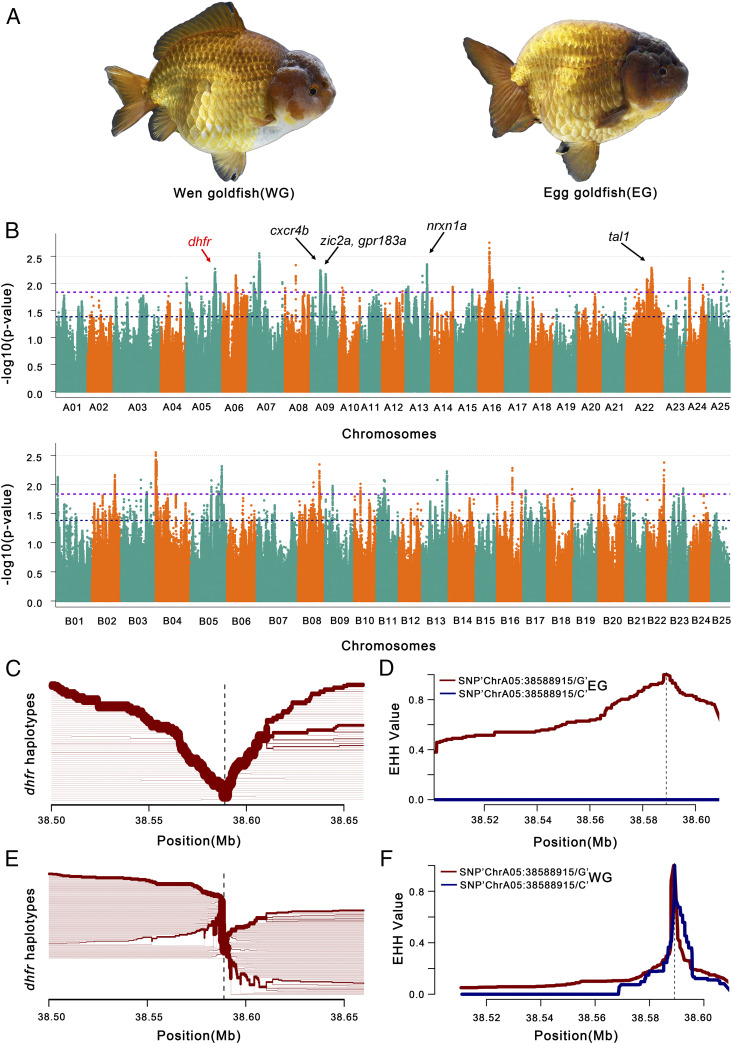
Fig. 4.
GWAS for dorsal fin-related traits in goldfish. (A) Pictures of Wen goldfish (WG, with dorsal fin) and Egg goldfish (EG, without dorsal fin). (B) GWAS for genes associated with dorsal fin in a Wen/Egg-goldfish population. Genes surrounding or within association peaks are indicated. Gene names are highlighted in bold black/red in candidate regions potentially related to dorsal fin development in goldfish. Representative candidate genes for dorsal fin-related traits include: dhfr (Cau.A05G0015640), cxcr4b (Cau.A09G0004970), zic2a (Cau.A09G0008030), gpr183a (Cau.A09G0007940), nrxn1a (Cau.A13G0000420), tal1 (Cau.A22G0009870), kif5ba (Cau.B02G0011950), and atp1a2a (Cau.B02G0012070). The chromosome number of subgenome A and B is colored with cyan and orange. The dashed lines show different genome-wide significance thresholds, respectively. (C and E) Haplotype bifurcation diagram in EG and WG subpopulations, starting from the two alleles at one of the representative significant GWAS SNP sites. The haplotype bifurcation diagram visualizes the breakdown of LD at progressively longer distances from the core allele from the focal SNP, which is identified by a vertical dashed line. The thickness of the lines corresponds to the frequency of the haplotype. We show the extended haplotype at the dhfr allele of EG subpopulation in C, relative to the shorter haplotypes at dhfr allele of WG subpopulation in E, which is in accordance with a selective sweep around the dhfr allele in the EG subpopulation. (D and F) EHH for SNPs “ChrA05:38588915” (diagnostic for dhfr) in EG subpopulation (D) and WG subpopulation (F) is shown with maroon line (for G) and blue line (for C), respectively.