Fig. 2.
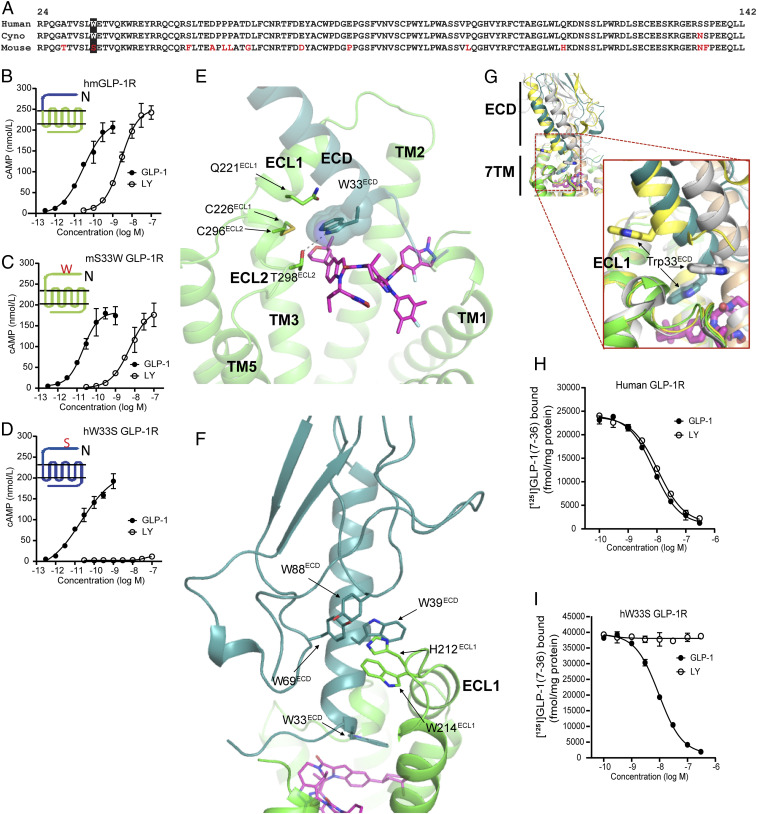
Trp33ECD mediates key interaction with LY3502970 and the surrounding region. (A) Amino acid sequence comparison of the ECD regions for GLP-1Rs of different species. (B) LY3502970 increases cAMP accumulation in HEK293 cells expressing a chimeric form of the mouse GLP-1R (domains shown in green) where the N-terminal 142 residues have been replaced by the corresponding region of the human GLP-1R (domains shown in blue). (C) Mutation of Ser33ECD to Trp33ECD in the mouse GLP-1R enables LY3502970 to stimulate receptor-induced cAMP accumulation, while the reciprocal mutation (D) in the human GLP-1R abolishes compound function. The chimera and mutant data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. (E) Trp33ECD interacts with LY3502970 and residues on TM2, ECL1, and ECL2. Residues and ligands are shown by sticks except Trp33ECD, which is also shown by spheres. Hydrogen bonds are indicated by dashed lines. (F) GLP-1R ECD orientation in the LY3502970 bound structure stabilized by aromatic interactions with ECL1. (G) The unique ECD orientation of ECD in the LY3502970 bound structure as a result of the unique Trp33ECD position. The structures of GLP-1R bound to LY3502970 (7TM in green, ECD in blue green, LY3502970 in magenta), GLP-1 (yellow, PDB ID code 6VCB), and peptide 5 (gray, PDB ID code 5NX2) are aligned. Trp33ECD is shown by a stick. Other peptide bound GLP-1R structures (GLP-1, PDB ID code 5VAI; ExP5, PDB ID code 6B3J) are not shown here, but their ECD orientations are very similar to GLP-1 bound structure 6VCB in yellow. (H and I) Competitive inhibition of [125I]GLP-1(7-36) binding to membranes isolated from cells expressing the human GLP-1R (H) or human W33S GLP-1R (I). Data are represented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.