Fig. 1.
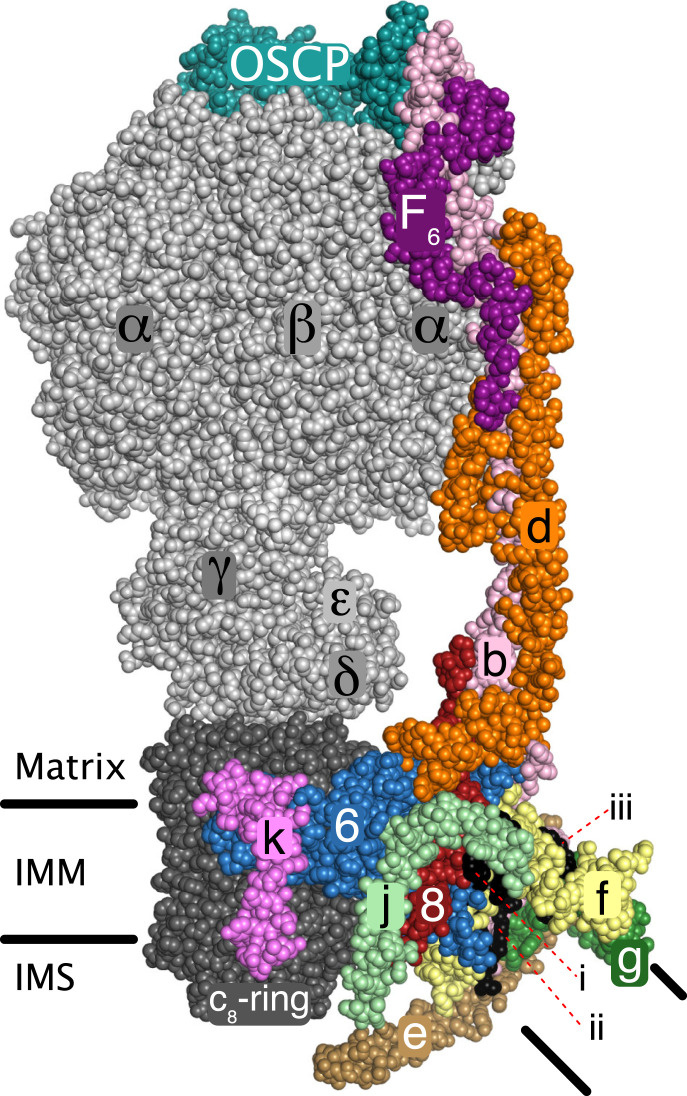
Organization of peripheral stalk and associated subunits in a monomer in dimeric ATP synthase in bovine mitochondria. The enzyme is inhibited by residues 1–60 of the inhibitor protein IF1, which is bound to the catalytic domain and not defined in the figure (4). Black horizontal lines represent the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) separating the matrix from the intermembrane space (IMS). The PS is formed from subunits OSCP, F6, d, ATP8 (designated “8”), and b. Subunit b has two transmembrane α-helices, residues 33–47 of bH2 and residues 55–73 of bH3 with an angle of 45° between them. The N-terminal amphipathic α-helix bH1 (residues 19–29) lies in the lipid head-group region on the matrix side of the membrane. These three α-helices form the scaffold for a wedge structure in the membrane domain to which subunits e, f, g, j, and ATP8, all with single transmembrane α-helices, are associated. Voids between proteins in the wedge are filled with five specifically bound lipids, three cardiolipins, and two other lipids, tentatively modeled as phosphatidylglycerols (4). The positions of one cardiolipin (defined as CDL1) and the two phosphatidyl glycerols (defined as LHG4 and LHG5) are indicated by i–iii, respectively. The wedge braces ATP6 against the c8 ring and in the dimer the two interacting wedges hold the rotatory axes of the monomeric enzymes at a range of acute angles via pivoting about the j subunits in the surfaces of the two wedges (4). Subunit j is involved in the monomer–monomer interface in yeast mitochondria (13), but the interactions are different from in the bovine structure (4). Subunits e and g make a separate domain not in contact with ATP6 (designated “6”) and subunit j, that may promote inner membrane curvature (33–35). Subunit k may be involved in tethering dimers together (5). The mitochondrial pmf drives the rotation of the c8 ring and the attached central stalk (subunits γ, δ, and ε) by the translocation of protons through the interface between the c8 ring and ATP6. The rotation of the central stalk carries energy into the catalytic sites of the three β-subunits in the F1 domain (subunit composition α3β3γδε).