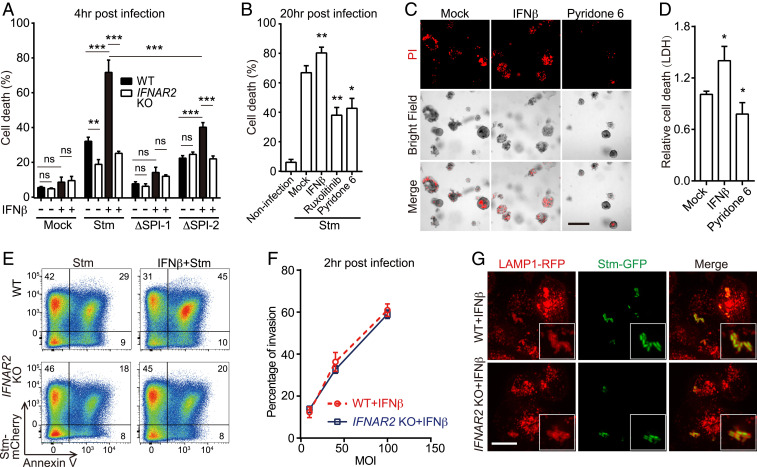
Fig. 2.
IFN-I promotes Stm cytotoxicity in IECs. (A) Survival of IFNβ-primed or IFNβ-unprimed WT or IFNAR2 KO HT29 cells 4-h post-WT or mutant Stm infection by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assay. (B) Survival of mock or drug-treated WT HT29 cells 20-h post-WT Stm infection. (C) Representative images of IFNβ or pyridone-6–primed or unprimed human small bowel enteroids 20-h post-WT Stm infection. Propidium iodide (PI) staining was used to detect cell death. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) (D) Enteroid survival 20-h post-WT Stm infection. (E) Flow cytometry of IFNβ-primed or IFNβ-unprimed WT and IFNAR2 KO HT29 cells 20-h post-mCherry-Stm infection and stained with Annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC). (F) Flow cytometric quantification of invasion of HT29 cells by mCherry-Stm. (G) Representative images of LAMP1-RFP-expressing HeLa cells 4-h post-green fluorescent protein (GFP)-Stm infection. Boxed insets depict higher magnification showing bacterial colocalization with LAMP1-RFP. (Scale bar, 10 μm.) Data shown are means ± SD from three independent experiments. See also SI Appendix, Figs. S1 and S2.