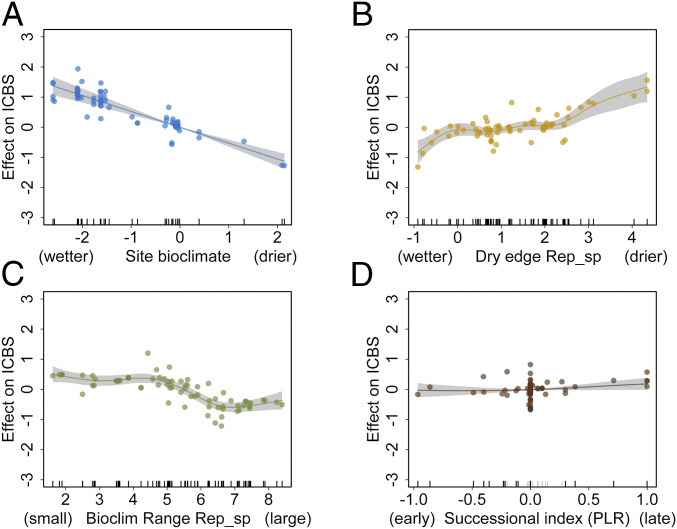
Fig. 6.
Contribution of (A) the bioclimatic characteristics of the study sites, (B) the dry bioclimatic edge of the replacing species (Rep_sp), (C) the range of the bioclimatic distribution of the replacing woody species, and (D) the successional index of the replacing species versus the dominant (predrought) species on the bioclimatic shift index. ICBS is the difference between the bioclimatic optima of the replacing woody species and the bioclimatic optima of the dominant (predrought) species along environmental axis 1 (Fig. 4). Positive ICBS values indicate shifts toward more xeric communities, whereas negative values indicate shifts toward more mesic communities. A shows a linear fit and B–D depict the component smooth functions of a generalized additive model fitted using the four variables depicted here; model R2 = 0.612, explained deviance = 67.2%; all variables are significant at P < 0.05.