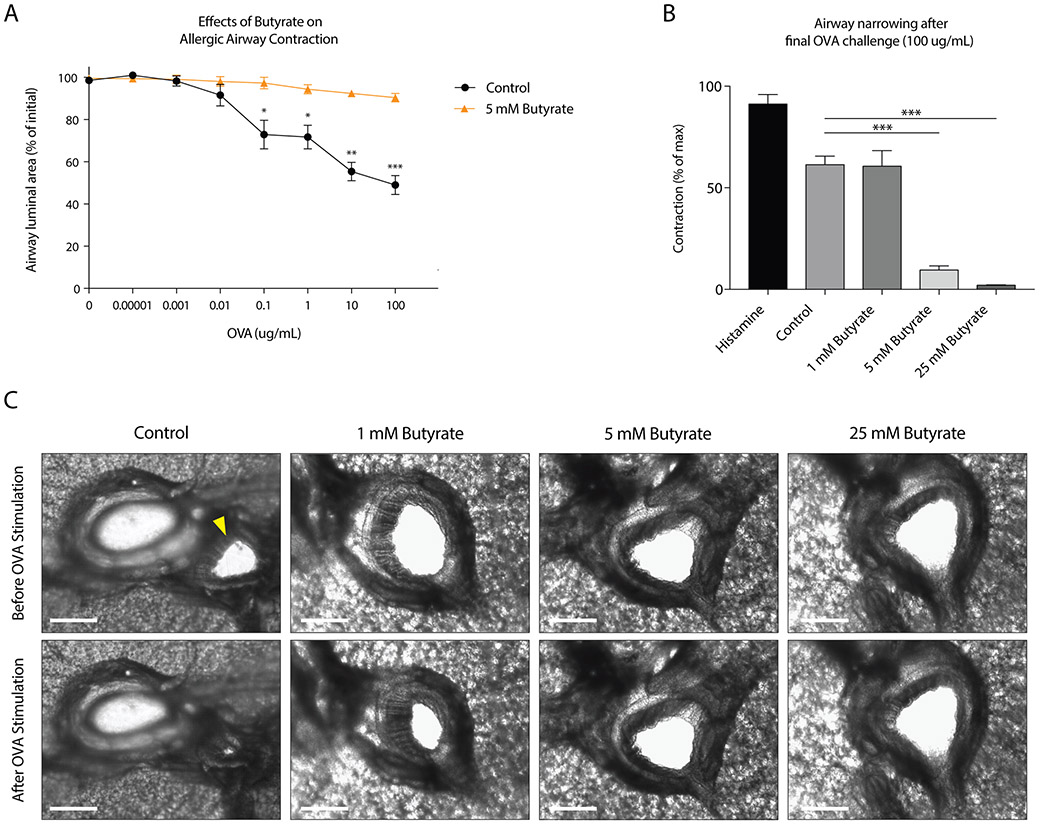
Figure 1. Butyrate inhibits OVA-induced airway contraction in an ex vivo model of bronchoconstriction.
A, OVA-induced reduction of airway luminal area in precision cut lung slices (PCLS) of OVA-sensitized guinea pigs either untreated or treated with butyrate for 24 h. B, Effect of different concentrations of butyrate on the airway luminal area after the final OVA challenge. As a control, slices were stimulated with histamine to induce strong contraction (1.84 mg/ml). C, Video stills depicting the effects of butyrate on OVA-induced airway contraction in PCLS. The white scale bar indicates 500 μm. OVA stimulation in vehicle treated PCLS induced strong airway contraction (‘control’). Note that the airway, indicated by a yellow arrow, is located close to a blood vessel. Pre-treatment of 5 and 25 mM butyrate inhibits OVA-induced airway contraction. Data represent mean ± SEM, statistical significance was tested using a (A) two-way ANOVA test or (B) one-way ANOVA test: Results in A and B are pooled from 2-3 independent experiments performed with PCLS from different animals (n=2-3).