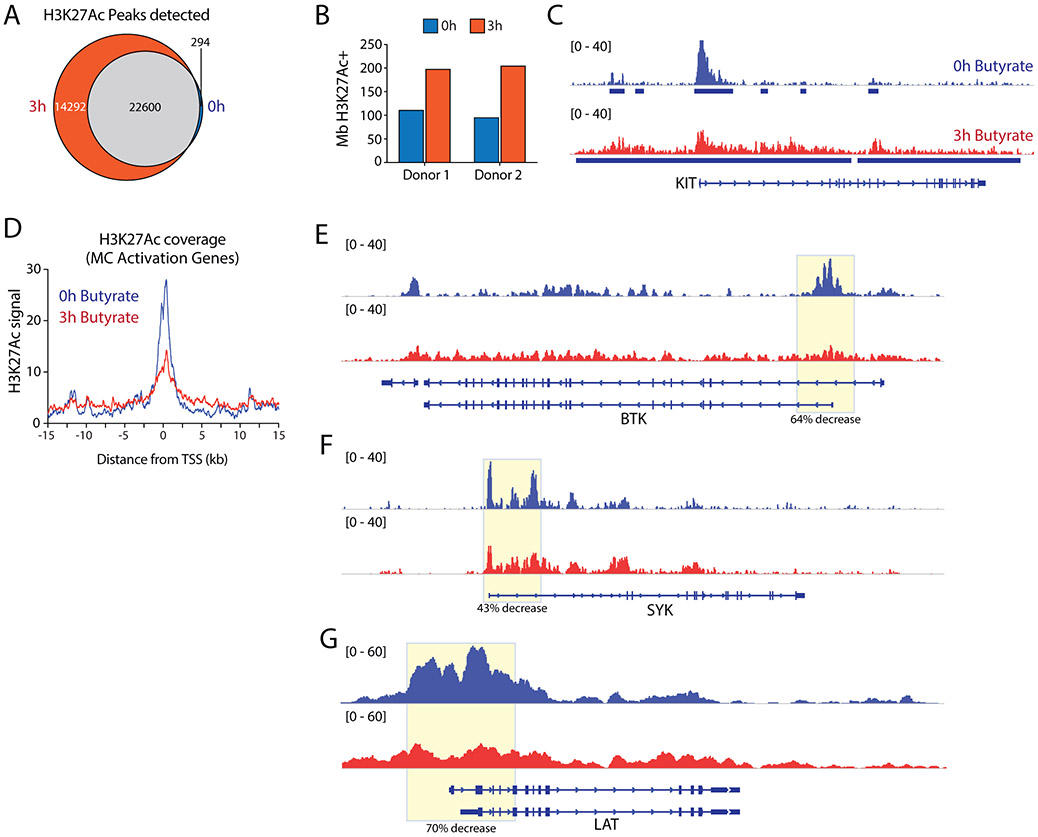
Figure 5. Butyrate induces a loss of histone acetylation at the transcription start site of key genes involved in FcεRI-mediated signaling.
A, Venn diagram depicting the overlap in H3K27Ac enrichment peaks (reproducibly detected in both donors) detected at 0h and 3h of butyrate treatment. Only a minority (~1%) of regions lose all H3K27Ac signal, in contrast to de novo enrichment of 14292 unique peaks following butyrate treatment. B, Butyrate treatment induces elevated megabases (Mb) of genome covered by H3K27Ac. C, Genome browser view of histone 3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27Ac) levels at the KIT locus, as measured by ChIP-Seq before and after 3h of 5 mM butyrate exposure. D, Average H3K27Ac levels around the TSS of mast cell activation genes downregulated by 24 hours of butyrate exposure (see Fig.4D). E-G, Genome browser views depicting H3K27ac levels across loci encoding key signaling molecules involved in FcεRI-mediated signaling. TSS regions show reduced acetylation levels for BTK (64% decrease), SYK (43% decrease) and LAT (70% decrease), correlating with their loss of expression upon butyrate treatment. Similar results were obtained using mast cells from 2 independent cultures of 2 different donors; data obtained from donor 2 is shown. TSS = transcription start site.