Fig. 1.
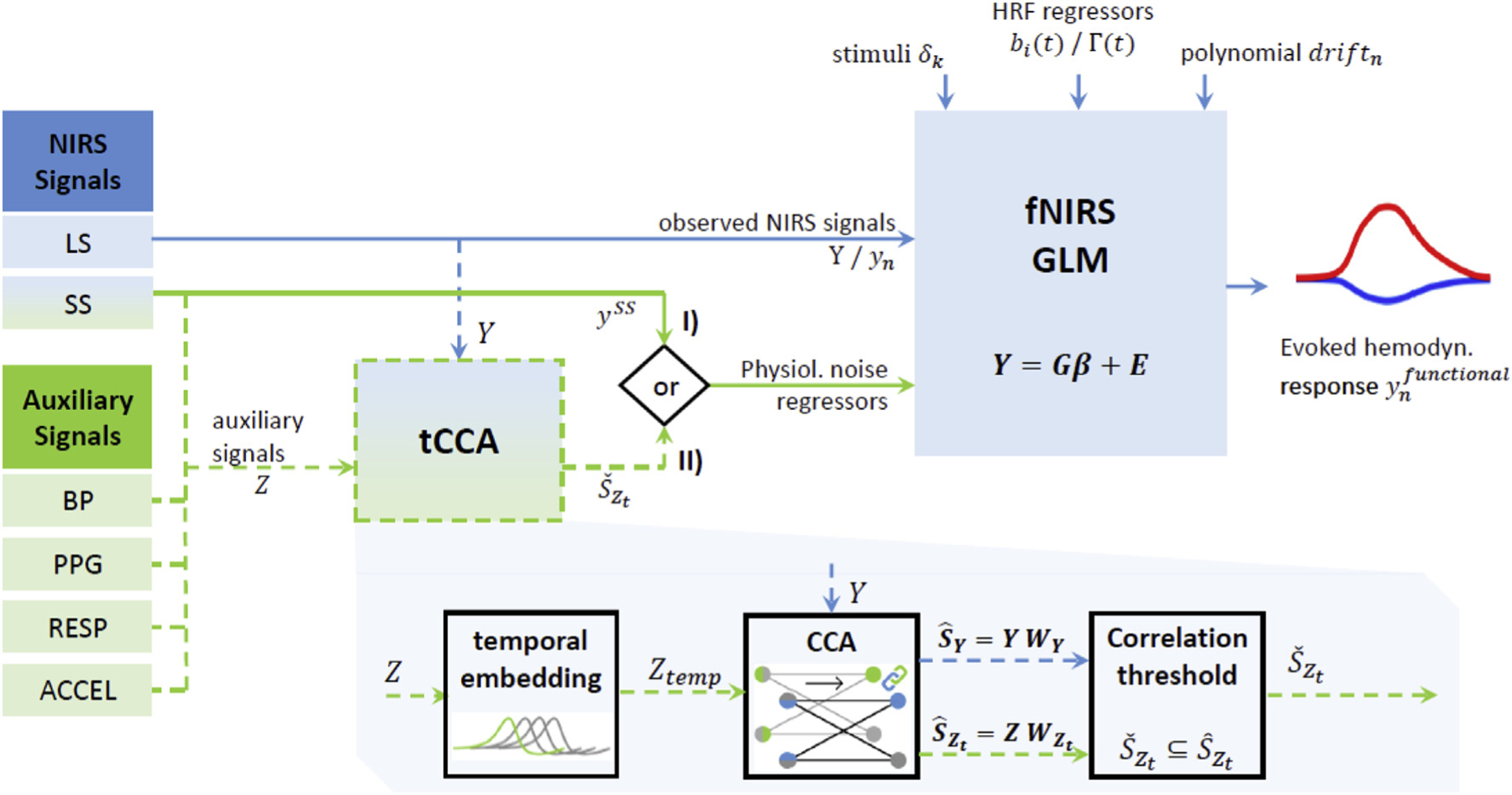
Extension of conventional GLM with SS regression (I) to GLM with tCCA (II). GLM recovers hemodynamic response function (HRF) estimates from observed Long-Separation (LS) fNIRS signals Y, using a priori knowledge of stimulus onsets and HRF and drift regressors. In the conventional GLM with SS (I), Short-Separation (SS) signals are used as physiological noise regressors to gain better HRF estimates . In the expanded GLM with tCCA, SS signals as well as other available auxiliary signals Z (BP: Blood Pressure, PPG: PhotoPlethysmogram, RESP: Respiration, ACCEL: Accelerometer) are exploited using temporally embedded Canonical Correlation Analysis (tCCA). Applying tCCA and a correlation threshold ρthesh yields physiological nuisance regressors in the tCCA source space that are superior to the standard SS approach. This improves contrast to noise ratio of the recovered HRF.
